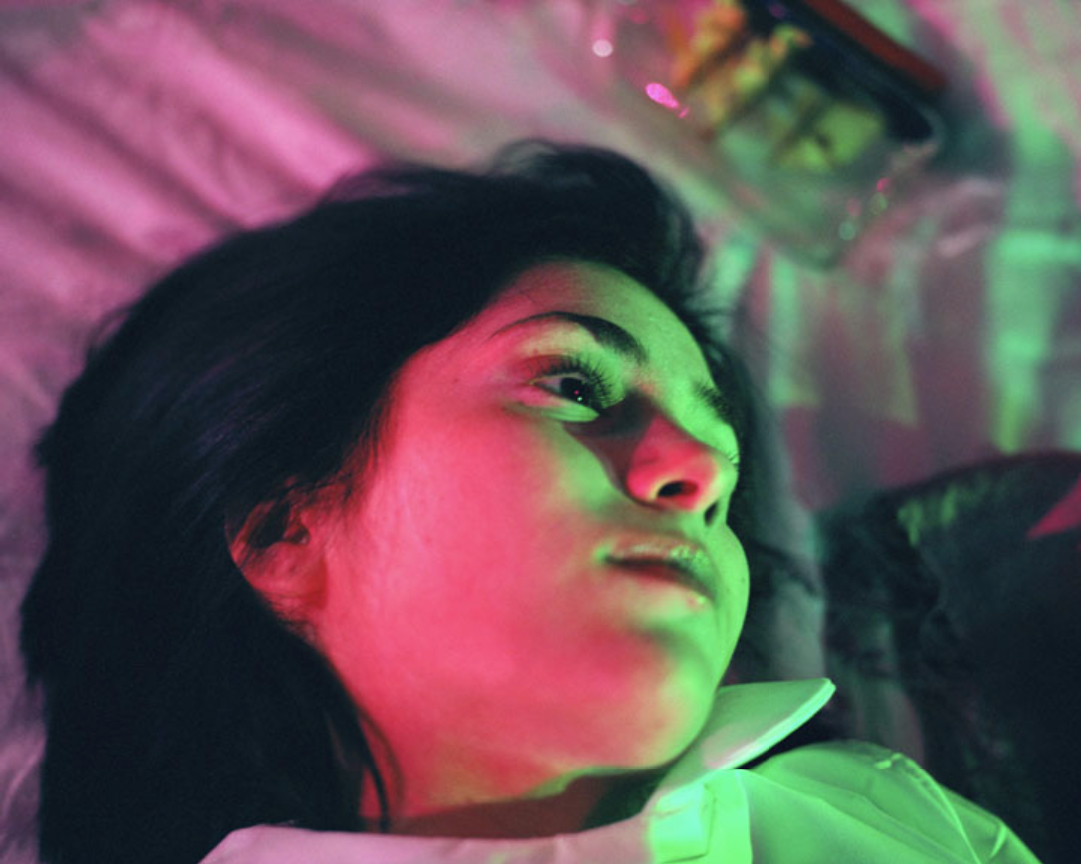
In the following interview, Brad Phillips speaks to author, Erica Garza about their mutual experience with sex and porn addiction. In Getting Off: One Woman's Journey Through Sex and Porn Addiction, Garza challenges the stereotype that sexual addiction is within a man’s nature, and for a woman, the result of sexual trauma. Recounting a life of “revolting” fantasies both imagined and realized, she lays out a lifetime of orgasmic pressure begging to be released, and courageously retraces her road to recovery. Throughout the conversation, Phillips and Garza share their experiences of responding to fans who look to them for guidance, the benefits of being triggered, and the sexual taboos that continue to plague our sense of moral authority.
BRAD PHILLIPS: I wanted first to say how happy I felt to discover your book. Having written about sex addiction myself, it felt valuable to read about a woman’s experience with participating and recovering from the same addiction. Particularly in that you wrote about it without nostalgia or redemption. What motivated you to write the book? Was there a sense that this was something you wrote in an attempt to process your experiences, or was it more of a desire to share with other people; make them feel less alone?
ERICA GARZA: It was a bit of both. I've always turned to writing as a source of comfort—a way to get troubling thoughts and memories out of my head and body, and onto the page. When I started writing about sex addiction, I did so in an essay online for Salon. I'd already been experimenting with telling my story in therapy and 12-step, but this was a more public telling. The response I received was overwhelming. So many people reached out and thanked me, and they were from all walks of life. I felt then that I could serve others by continuing to write about this. We aren't often presented the opportunity to help a wide range of people, and this was my chance.
PHILLIPS: Sometimes there's trouble in writing about personal subjects that are taboo, in that readers develop projections about you, and a sense of attachment. Have you had any response from people who felt like they were connected to you in a way that felt creepy? I also was curious if men reached out to you, ignoring the aspects of shame and recovery you write about, and simply saw you as someone “into sex,” and approached you that way. Has that happened?
GARZA: Several men (and a few women) have reached out to me because they see me as someone “into sex.” This ranges from unsolicited dick pics, to requests to meet up, to full-blown erotic stories they want me to read. I usually block them immediately, or if I have the energy, I tell them they’ve crossed a boundary and we have a discussion. But I receive more messages from people looking for help because they’re dealing with sex/porn addiction. I always try to acknowledge and address these messages because I know how isolating addiction can be. I usually direct them to 12-step meetings because they can offer connection and community, but sometimes this isn’t enough for them. Some people reach out to me as if I’m a therapist, as if I have the magic solution to their pain, and this can feel overwhelming. I am not a counselor. I’m just a person who shared my story as honestly as I could. They have access to this honesty too. The best I can do for those who put me on this pedestal is to bring myself down to eye level. To remind them that I’m just as vulnerable as they are. The biggest difference is that I’ve come out of the shadows—maybe they should too.
PHILLIPS: It’s interesting and disappointing that people might read your book and completely miss all the shame and intense pain you discuss; things which go hand-in-hand with addiction. You mention other people coming out of the shadows. I think that there are certain people who find the shadows themselves sexual. I feel like on some level there would be very little new information to discover about men coming out of the shadows, which again is why I think your book is important. You’ve done mainstream press, and mentioned to me that you were told there were certain words you couldn’t use, or certain parts of the book better left not discussed, because they could ‘trigger’ someone. How do you feel about this climate, where we’re told we need to prevent triggering strangers?
GARZA: I tend to disagree with the sentiment that there’d be nothing new to discover by men coming out of the shadows. I think the act of telling can help the addict discover a world of new information about who they are or what they want. And other people can be positively affected by hearing these confessions, because they too can confess without fear of judgment or criticism. As far as people being triggered by stories of addiction and sexual language, I’m sick of it. It reeks of Puritanism. We can watch zombies eat off people’s faces on prime-time television but we can’t see breasts. What does that tell us about what we fear as a culture? Our own animalistic primal nature? Our complicated desires? Our grip on control? When I’m triggered, instead of acting out or shutting down, I become curious. Why am I being triggered? What is being reflected to me? By asking questions like these, I learn more about myself.
PHILLIPS: Censorship and the aversion to natural female bodies on Instagram is insane to me. Curious is a good word my therapist uses, it helps take the shame out of self-reflection. I think the complication of desire can feel scary to express because really, we’ve never seen it done. When you say animalistic, do you think it’s elemental to our fear of expressing all the ways we’re still animals?
GARZA: Maybe being reminded of our bodily functions and the natural impulses we share with animals only reminds us of the other most natural physical experience we fear most—death. If we stick with our intellect, we can form elevated ideas about what’s right or wrong, and we can let religion and the media tell us how to desire and how to express that desire in the same way that religion and media tells us that we don’t have to die. But I think all of that is a distraction from being present in our mortal bodies, accepting and indulging our natural impulses.
PHILLIPS: Having once been close to death I’m no longer afraid of it. That hasn’t helped in managing my daily unease though. I recently read, for a radio show, the entire list of paraphilias from the DSM-5. What shocked me was that the only two paraphilias classified as mental illnesses were sadism and masochism. I’ve seen it be particularly shaming for masochists, especially women, to be told that what they like in bed makes them ‘wrong’ in multiple ways. There is a lot of very quiet research around the idea pedophilia is an innate sexual preference in the same way that homosexuality is. The recidivism rate for pedophiles offenders is above 99 percent. But these are the pedophiles that offend. There are far more that don’t, and by default are repressed. Sympathy for the pedophile isn’t something people want to get behind. Maybe you could tell me how you think these more ‘extreme’ sexual predilections could be managed, or re-evaluated.
GARZA: I think the fear of things like child sex dolls and cartoons for pedophiles mirrors the fear that some have about tolerance to porn, not just the most extreme kind. If you see images repeatedly, those images might lose their charge and so you’ll need more extreme images to feel something again. Pedophilia is one of those subjects that upsets people because the trauma can be devastating and I understand why people shy away from the subject because they are trying to prevent any more harm being inflicted upon those who’ve suffered. They want, justifiably, compassion to be directed to the victims. But I do think that there is value in trying to understand the pedophile’s motives, by conducting more research, and by including them in the discussion. As difficult as it may be to hear their stories and understand the why of what they do, the better equipped we are to prevent future incidents of harm. I think when something has been deemed socially unacceptable and there’s so much fear around the thing that we won’t even talk about it, then it’s a good indication that we MUST talk about it. Silence eventually implodes and the aftermath is rarely pretty.
PHILLIPS: Long ago Susan Sontag predicted ‘image fatigue,’ which she related to the Vietnam War photographs being relayed back to American viewers, and how they would eventually lose their impact. That same thinking can definitely be extended to pornography and the absolute nadir it exists at in 2019. I agree with you and have tried myself to address the idea that if things are uncomfortable or difficult to talk about, then it does mean we should. There is difficulty in seeing both the victim of a crime and the perpetrator as two separate people involved in a scenario from which information could be gleaned.