text by Adam Lehrer
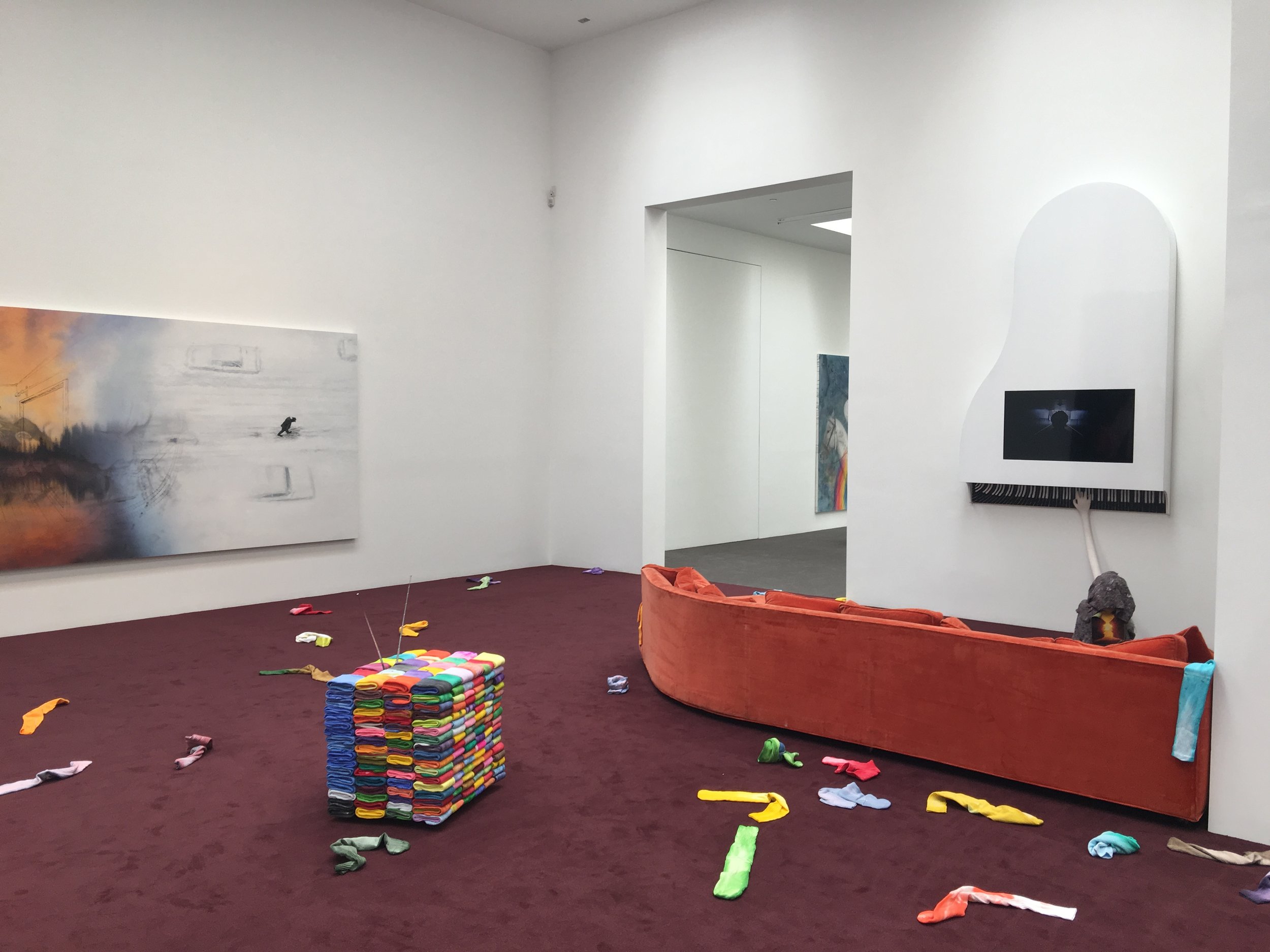
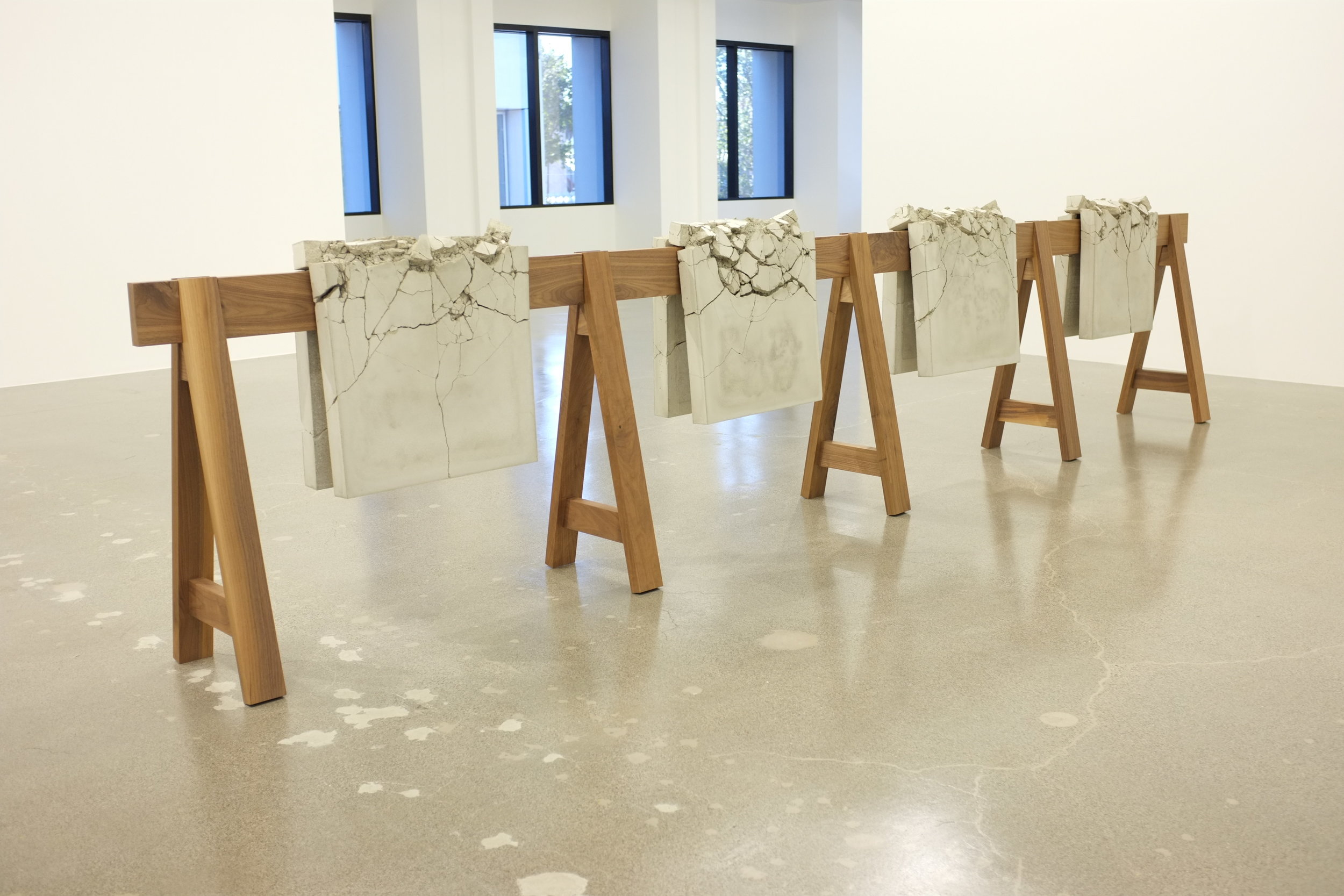
The color palette used by Los Angeles-based abstract painter Mark Bradford for the work in his stunning new show at Hauser & Wirth, Be Strong Boquan, is different than the palette that comes to mind when I think of his other work. While some paintings make strong use of the dark and austere colors most associated with his work, there are also bright pinks and yellows. Despite the vivaciousness of these colors, there is still a physical menace that emanates through them. Walking through the exhibit, I was reminded of that indescribable feeling that courses through your body just before you realize that you are full-blown sick: goosebumps on your arms, chills running through your spine, the inability to make a fist, a feeling of faintness.
The feeling elicited was not at all unintentional on the part of Bradford. Bradford has the uncanny ability to filter societal woes through abstracted images. In Be Strong Boquan, Bradford tackles issues personally important to him: society’s false representation of the queer identity, the brutality of the 1990s race riots in Los Angeles, and the AIDS epidemic in the early 1980s. The show seems emblematic of the fear of the deterioration of the body, and the militant efforts to destroy the bacteria and disease that infect the body.
Despite the heavy subject matter of his work, Bradford’s persona is anything but dark. Standing at about 6 ft. 5, Bradford has no problem talking about his work. In fact, he revels in it, and loves gauging the reactions of those that observe and examine it. He did just this the day of his opening. Walking a group of collectors, admirers, and journalists through the exhibition, Bradford illuminated on some of his conceptual choices for the show. These are some things I learned about Bradford.
Bradford harkened back to 1980s club culture for the show, capturing the exuberance of the scene, contrasted with the AIDS epidemic that was slowly, and later quickly, killing off the peoples that made the scene exuberant in the first place:
“In this show, maybe I was thinking about this space being the Roxy a little bit, but then I was also thinking about nightlife and what was on the horizon as far as the epidemic that was on the horizon, as in the AIDS epidemic. Interestingly enough, Hauser and Wirth kept all the roller skates from the Roxy and they shipped them all to my studio about a year ago and I kind of hung them from all the rafters and would roller skate around to find something abstracted in the social.”
When you walk into the exhibition, the first thing you will hear is the song‘Grateful’ by 1980s Disco performer Sylvester that is accompanying the piece ‘Deimos,’ a video installation. It gives you the feeling of the substances just starting to wear off and the lights going out at the club: the possibilities of the night coming to a screeching halt. Of course this is amplified when you realize the rest of the exhibition deals with possibility snuffed out by disease. Fitting then that the exuberant track is being performed by a musician who tragically lost his boyfriends to AIDS, neglected to get treatment himself out of devastation, and slowly saw his own body deteriorate.
“The song is ‘Grateful’ by Sylvester, I think Sylvester was in many ways ahead of its time. Anybody who lived through that time is grateful, I feel, just to be here.”
Though the exhibit does not explicitly depict the human body, the body is ominously present in each of the paintings and the sculpture.
“The marks that you see are cells that I looked at under a microscope that just became marks. The show does have to do with the body even though the body isn’t present. It’s more like a ghost body.”
He is interested in the time it can take for a monumental social plague, such as AIDS, for people to come together and speak out against the plague in a social setting. “With the AIDS crisis in the ‘80s, it was pure dying. It was almost political, God came down and brought this disease and it just wiped everyone out. In the ‘90s it started to get political. I’m interested in the military terms we use when it comes to things that deteriorate and infect the body. “We have to wipe this disease out.”
He has become interested in processes that involve waiting and time, particularly his stain paintings that make use of tracing:
“I used to work at a hair salon, and I used to trace the prices on the wall. Sometimes I reduce my palette. It’s like when you have a heavy meal so next you want to eat a salad and drink some tea. Sometimes I feel like my work can be so heady, so material. So I’ve been doing the stain paintings, where I use a reduced palette and it can become all about the trace and all about the times. You do the paintings in about a two-hour time. As this aged black paper, you pull it off, and it leaves traces. I like that even though it’s a very reduced palette, it has a lot of depth.”
The final piece in the exhibition, ‘Spiderman’ is a play on the black comedy best exemplified by Eddie Murphy in the 1980s. Murphy and other comedians often used homosexuality as joke material. The piece features video and the voice of an unseen comedian, a transgendered man. The piece forces us to confront our complicity in hate speech by laughing about dark jokes concerning Eazy E’s homosexuality (“Only Eazy-E can make AIDS gangsta,” says the unseen comedian) and the black community’s battle with AIDS. Bradford is interested in comedy’s ability to offend while simultaneously getting people to talk about uncomfortable issues.
“I remember watching Eddie Murphy’s ‘Delirious’ in the early 1980s. I wasn’t really interested in Eddie Murphy, really. But I’m always interested in the developing of the social contract. Like the “n” word. It is a part of the social contract now, but there was a time when it wasn’t taboo. When does something stop being taboo? I remember Eddie Murphy making jokes, “faggot look at my ass.” Everybody was just laughing! I thought if this is the early part of the AIDS epidemic, and this is now part of the social contract. What I often find is I like to turn comedy around. Like making the man the butt of the joke. I wanted to address social change. I do think there are things that just aren’t appropriate, like calling black women bitches and ho’s.”
Bradford’s work is compelling in its aesthetic beauty contrasted by its conceptual heaviness. He doesn’t know how to make art any other way.
“I’ve seen a lot of hard stuff in my life, and I’ve seen a lot of beautiful stuff in my life.”