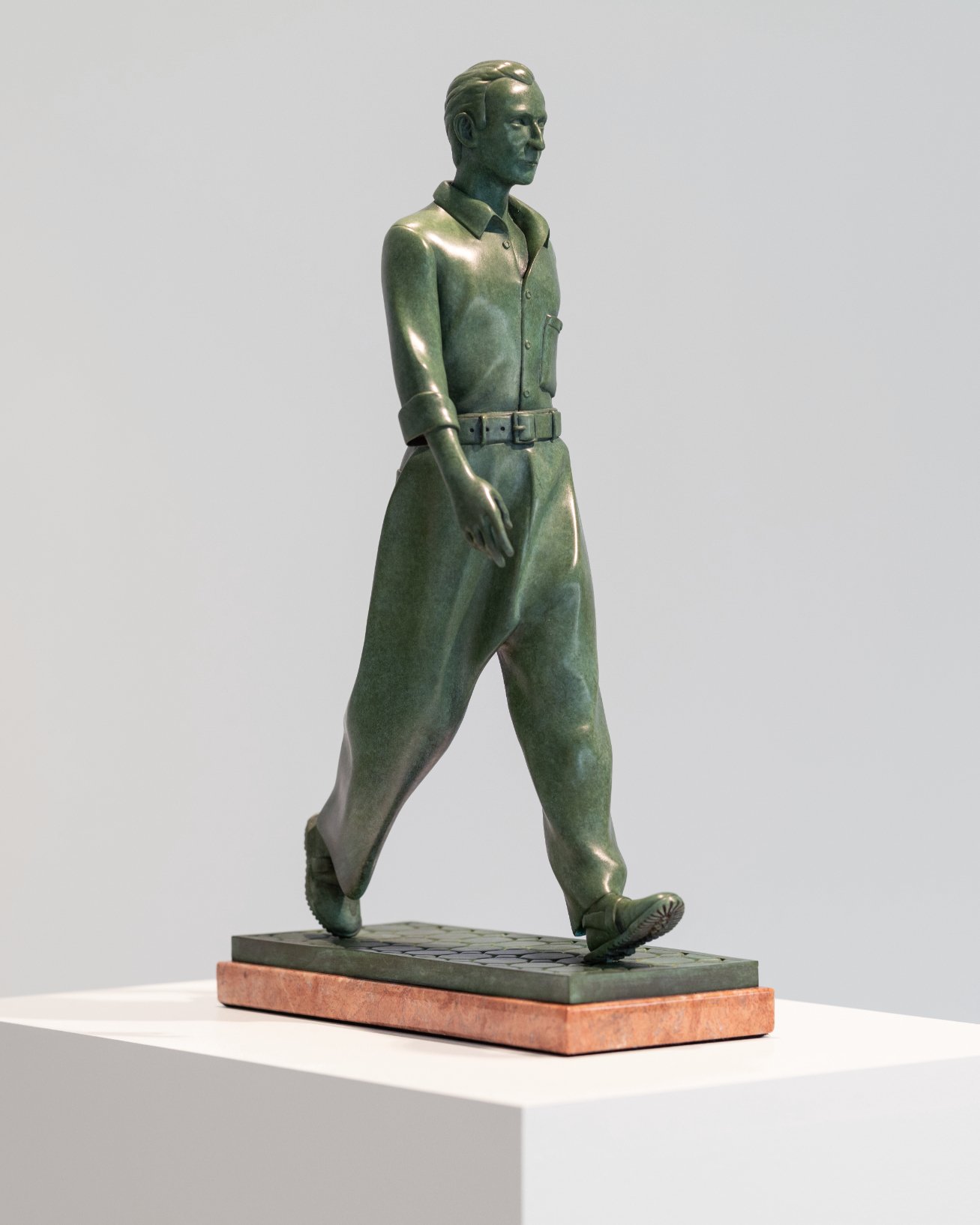
Everett Sloane in Yohji Yamamoto S/S 2000
photograph courtesy ofstudio photography
interview by Isabelle Albuquerque
photographs by ofstudio photography
If you look up close and if you have an exceptional memory for Old Hollywood character actors, you will clearly make out the distinctive face of Everett Sloane with his signature wide-set eyes and crooked nose. Known primarily for his roles in The Twilight Zone, The Andy Griffith Show, and Citizen Kane, the actor, songwriter, and theatre director took his life by way of barbiturate overdose in 1965 at the age of 55. Here, he is immortalized and miniaturized by artist Nicolas G. Miller in the form of a bronze statuette. He appears to move with a brisk, yet cool stride walking down an imaginary runway wearing Yohji Yamamoto S/S 2000. In the following interview, Isabelle Albuquerque sits down with Miller to discuss the temporality of fashion, the process of sculpting in bronze, and the act of breathing life into the deceased.
Isabelle Albuquerque: How did art first come into your life?
Nicolas G. Miller: My first memorable experiences with art were of the work of my maternal great-grandfather, Orville J. Hanchey. He was a painter, educator, and all-around bon vivant. When I was very young, I was lucky enough to visit Orville at his home. He was already quite old when I visited and had retired from his post as Professor of Art at Northwestern State University in Natchitoches, Louisiana. He lived in a small house that was stuffed with his paintings and all manner of marvelous objects. Orville's paintings are delicately rendered watercolors of flower arrangements. There were two that hung in my childhood home. I recall staring at them often and wondering how he was able to make the petals of lilies look so beautifully diaphanous. And, to be honest, I still don’t know how he did it!
ALBUQUERQUE: Oh how beautiful. Thinking of the petals of his lilies makes me think also of the draping of the Yohji pants in your sculpture Everett Sloane in Yohji Yamamoto S/S 2000. I’m obsessed with how they fall. How the fuck did you do that?
MILLER: Thank you very much, Isabelle! The trickiest thing about sculpting my statuette was the clothing. The majority of examples I’ve seen of sculpted clothing are from classical art. In other words, it is all tunics. Not pants, lugged sandals, button-up shirts or high heels. I knew in this piece, since it was Yohji, the pants would be the main attraction. I aimed to keep the viewer entranced as their gaze glides along the surface of the sculpture. There is a technique developed in the 1990s by the automobile designer Chris Bangle when he worked for BMW called “flame surfacing”. The idea was to use compound curves to mimic the form of flames on the exterior of sports cars. The 2003 BMW Z4 stands as a good example. When a flame-surfaced automobile drives by at night, pools of light form along the compound curves creating a pleasing visual effect similar to watching a log burn in a fireplace. I was hoping to achieve this effect, but at the scale and speed of sculpture, particularly the Yohji pants.
ALBUQUERQUE: Of course, you flame-surfaced them. Ha! When did fashion first begin to emerge in your art?
MILLER: That is a very interesting question. I am a sculptor and sculpture is generally preoccupied with questions of space (scale, proportion, site, etc). Fashion, on the other hand, seems bound up with questions of time (seasonal releases, the cyclical recurrence of styles, etc). I have always been drawn to works of art that attempt to present contradictory terms. Fashion entered into my sculptural vocabulary as a way of asking questions about time and temporality within sculpture.
ALBUQUERQUE: Yes, exactly. And the way you connect to particular seasons and collections in fashion allows the work to both act as a time travel object and also have a discrete connection to a specific moment in time. Speaking of a specific moment in time—what are you wearing right now?
MILLER: I am at home and am wearing a black cotton sweatshirt. On the sweatshirt is a white screen print of an image of downtown Los Angeles. Two impossibly large palm trees are superimposed on top of the cityscape, and just above the palm trees are the words "Los Angeles, California." It is the sort of sweatshirt you buy as a souvenir on Hollywood Blvd., which is precisely where I bought it. Below that I am wearing black polyester athletic shorts manufactured by Kappa and designed for Napoli SSC, a professional soccer team based in Naples, Italy. It is the kind of outfit I put on without thinking too much.
ALBUQUERQUE: Ah! Yes! Superimposed palm trees forever. I love Hollywood Blvd and visit its souvenir shops often. Jon and I used to make posters for our music shows on top of old signed glamour shots from unknown actors. There is so much longing and loss in those images. What made you decide to work with actors who are no longer living in clothes made decades after their deaths?
MILLER: This piece is one in a series of sculptures of old Hollywood actors dressed in new clothes. Each of the actors were well known in the first half of the twentieth century. In their sculpted form they will all be wearing runway looks from the year 2000. It is important to me that the clothes were designed after the actors had passed away. This structure has an internal logic that reminds me of the logic of fashion, wherein two disparate moments are brought in close proximity to one another. I hope the impossibility of these combinations gives the viewer a sense of temporal vertigo. Vertigo is frequently associated with a sensation of spatial imbalance. It is often described as "the world around you spinning." Recently, I have the sense that the world around me is spinning, but through time rather than space.
ALBUQUERQUE: Yes. I know exactly what you mean. How does bronze hold time for you?
MILLER: As with so many materials the more I look into bronze the less clearly it signifies. On its surface bronze is meant to imply permanence. Yet the history of bronze sculpture in Europe is one of constant change and impermanence. Large, bronze public statues were erected to symbolize new world orders, but were often melted down to make weapons to fight wars. Despite the common sense that bronze implies permanence, it is far more plastic than one would first think.
In the act of making this piece at a foundry I was struck by a sense of eternal return. In the lost-wax process of producing a bronze sculpture, first the sculptor makes a maquette. The maquette is then destroyed in the process of making a silicone mold. Then the silicone mold is used to produce a wax version of the maquette. This wax version is encased in an investment mold (a hard concrete-like substance). Then the wax is melted out and bronze is poured into the investment mold. Finally the investment mold is destroyed in order to reveal the bronze. At each step of the process, the objects created in the previous step are destroyed. This gives the final product the effect of permanence, which reminds me of the logic of seasons and the return of styles in fashion.
I imagine the final resting place for my statuettes to be a domestic setting. Perhaps atop a mantel. Another common object that sits on a mantel is a clock. As time passes, the outfits sculpted into the bronze statuettes, and perhaps the actors too, will go in and out of fashion, not dissimilar to the way that the hands on a clock go round and round.
ALBUQUERQUE: Wow. Yes. I love thinking about the impermanence of bronze and the lost wax casting process. Even in the name of the process we have the word, lost. With the last few years in lockdown, I think we’ve all been thinking about lost time and life. The hands on the clock going round and round for real. How do you breathe time and life into people who are no longer with us? Since these actors were alive before scanning technology, do you work from photographs/film stills/collective memory?
MILLER: I sculpt in a 3D software called ZBrush. This software was developed to give the feeling of sculpting in digital clay. I learned a technique for sculpting portraits in ZBrush from a digital sculptor who worked at Industrial Light & Magic. When it came time to choose a subject, all of the other students in his course selected contemporary Hollywood actors. At first I thought this was simply in keeping with the general culture of "digital art," but there is a much more practical element to it. In order to sculpt a portrait properly in ZBrush, you need a great number of reference images. Preferably images taken from many angles.
At first, I thought I would sculpt one of the Fayum portraits from the 1st century AD. The Fayum Portraits were painted on wood and buried with upper class mummies from Roman Egypt. The depictions are truly haunting. Since the paintings were intended to be buried with their subjects, neither the painter nor the sitter imagined a future where the pictures would be seen by posterity. This idea of an image without a future feels so foreign to me. I quickly realized that sculpting from these images was too difficult and that the Fayum portraits are probably best left as paintings.
I then began working with old Hollywood actors. I make large collections of promotional photographs and film stills of each actor before I begin sculpting. What I realized when I started to manipulate the digital clay is how very different a face can look when shot under different lighting and with an assortment of camera lenses. My statuettes end up as montages of the faces of bygone actors—many moments condensed into one.
Everett Sloane in Yohji Yamamoto S/S 2000
photograph courtesy ofstudio photography
ALBUQUERQUE: Yes! You can really feel that in the work. Is there significance in the sculpture’s smaller-than-life scale?
MILLER: The scale is of utmost importance to me! In France, during the Art Deco period, there was a preponderance of small figurative sculptures—also known as statuettes. Many bronze foundries opened in order to keep up with the demand from the rising bourgeois class for bronze art. These statuettes were anywhere from sixteen to twenty-two inches and intended for domestic display. The economic structure of companies such as Susse Frères or LN Paris JL is very interesting to me. They both had foundries in the countryside and exhibition spaces in the city. Both foundries supported a large network of figurative sculptors by commissioning maquettes that they would sell in editions.
This moment was also ripe with promises of grand technological advancement. There was growing optimism around electroplating, which claimed to provide a thin seamless layer of precious metal atop any sculpted form. The fantasy was that it would remove much of the need for human labor from the process of making a fine metal sculpture. When I came across this moment in the history of European sculpture I was deeply struck by the similarities to our time, in particular the promises of 3D technologies and their applications in sculpture.
Susse Frères would produce beautiful catalogs for customers filled with photographs of their statuettes. I am making advertisements for posters and magazines of my statuettes as a way of drawing out similarities between the moment of Art Deco statuettes and my own work. I also want to allude to the possibilities for sculpture in a model like Susse Frères.
ALBUQUERQUE: Very cool. Now that you have released the little man into the wild, what are you working on next?
MILLER: Lupe Vélez in Hussein Chalayan S/S 2000.
ALBUQUERQUE: AHHHHHHH Cannot wait for her.