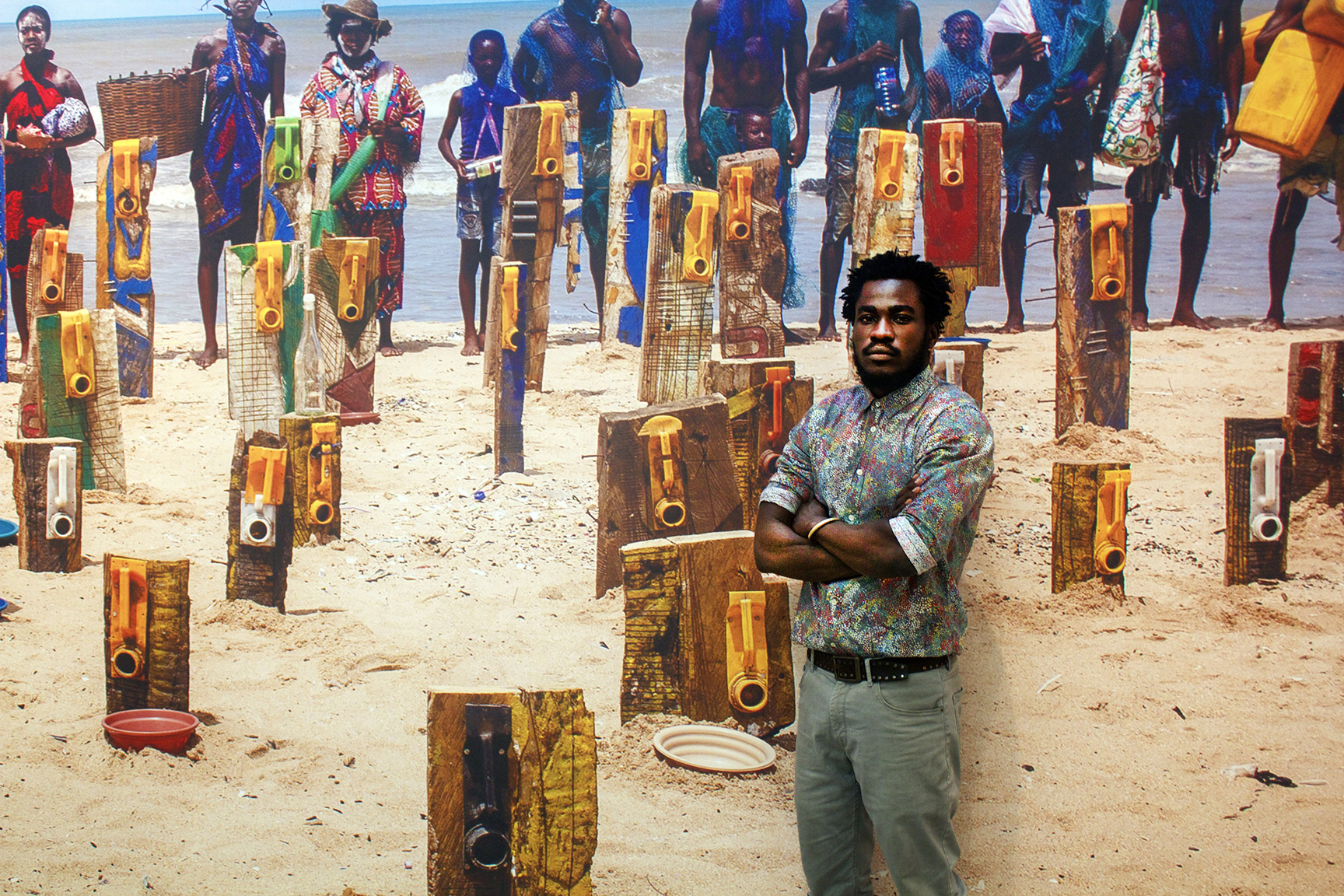
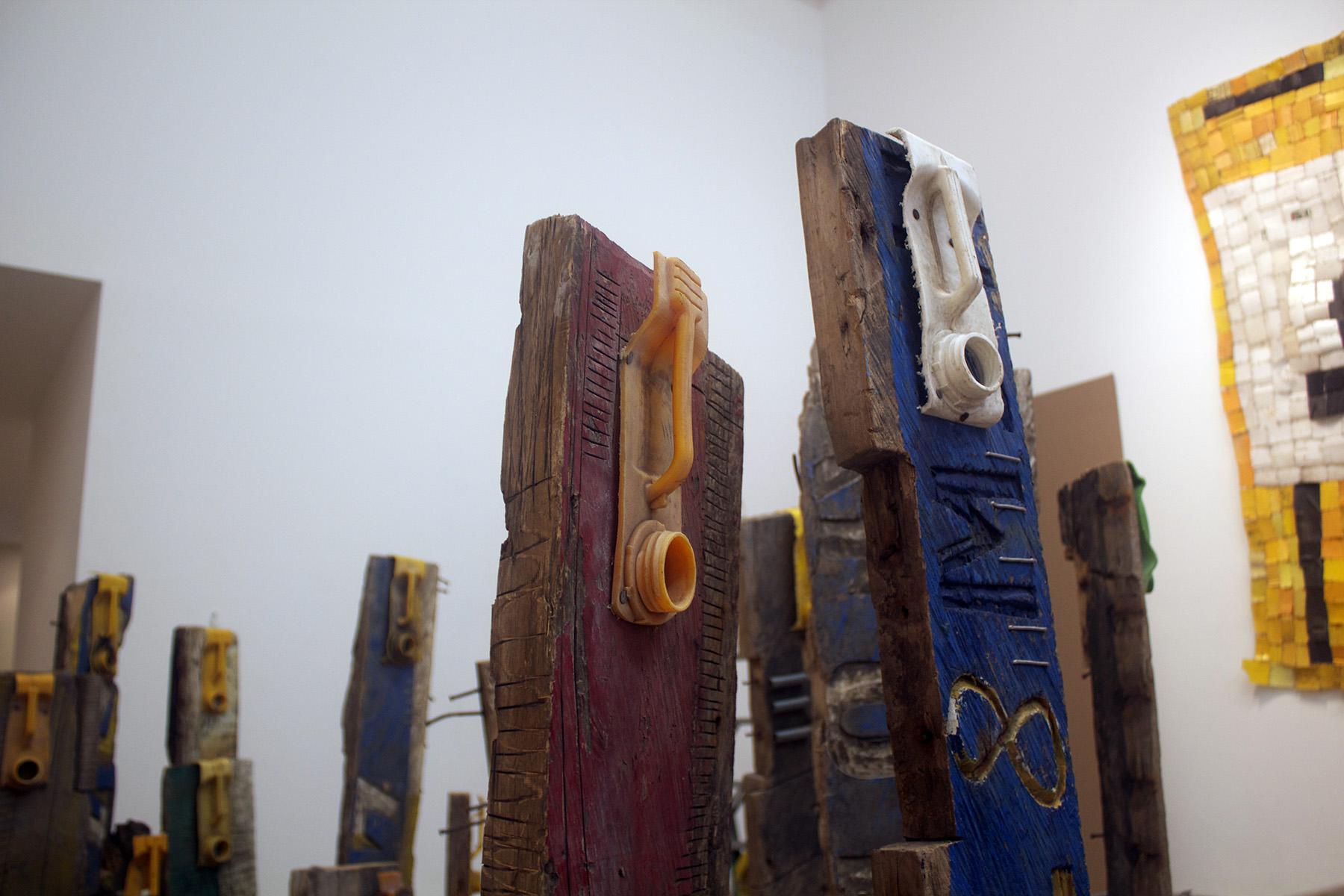
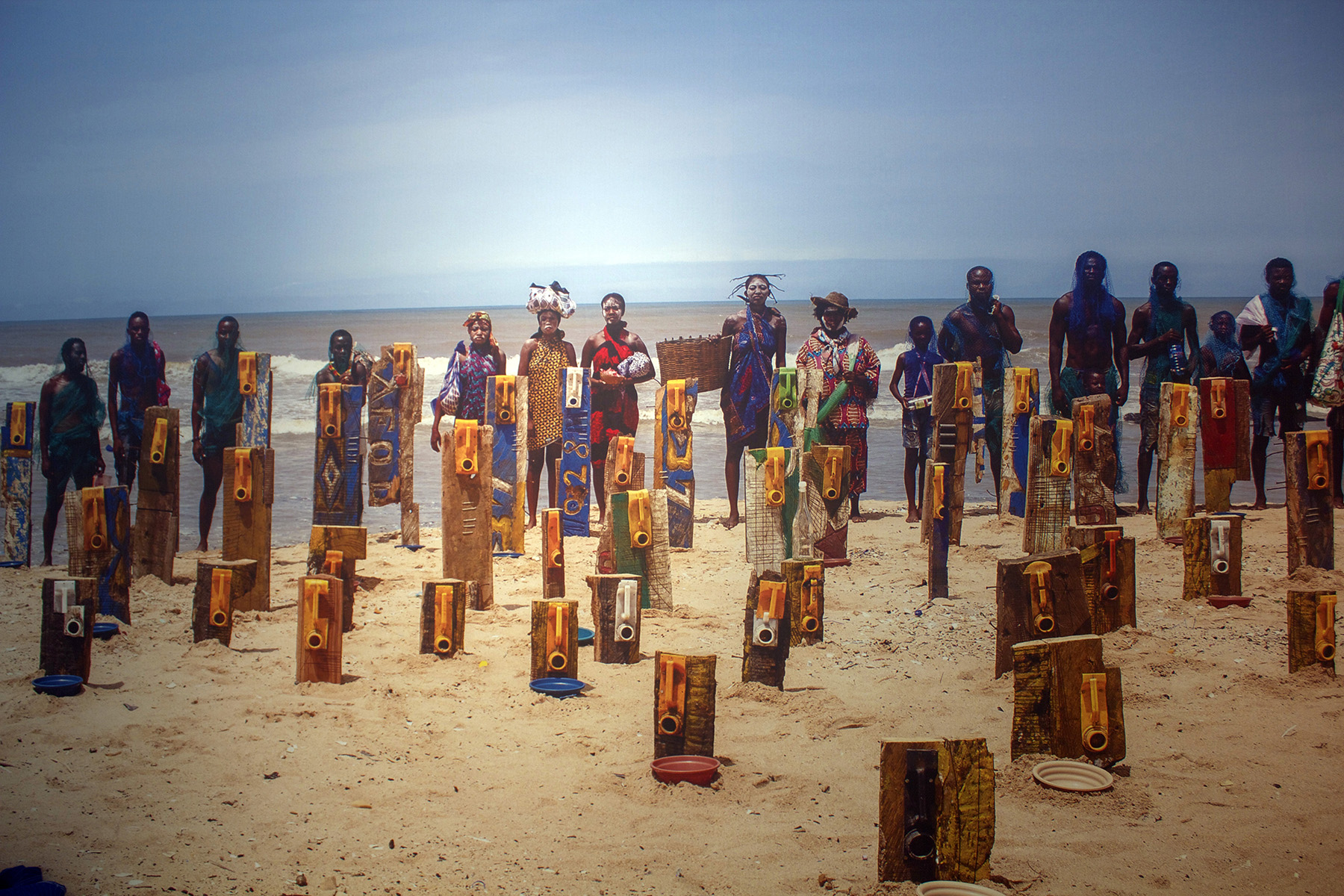
There are not a lot of artists willing to get dragged by a noose through the streets of Accra, the capital of Ghana, in the name of social justice. Gallon by gallon, Ghanaian artist Serge Attukwei Clottey is returning your used plastic refuse in the form of beautiful masks and mask-like sculptures that take on haunting human expressions. In the artist’s native Ghana, yellow canisters are ubiquitous and have become a seamless part of the country’s landscape. Where these containers come from has become a source of plight for the people of Ghana and central to Clottey’s artistic practice. Originating in Europe, the containers once held cooking oil, but after a water shortage, the containers were repurposed to hold water and gasoline. Over time, though, the gallon jugs have become so plentiful that they have started to pollute the beaches and even landfills. Clottey has coined the term “Afrogallonism” to describe this exercise and it has, over the years, become his rallying cry. Indeed, there is something very punk in what the artist is trying to achieve. Many of his sculptures come from works created by Clottey for his performance collective GoLokal, which has held numerous public presentations that have to do with displacement, migration, colonialism and Africa’s place in the treacherous nexus of a vastly globalized world. A land rich with resources, but flooded with greed. Footage of Clottey being dragged through the streets by a noose while performers throw money at him was replayed multiple times a day for a week straight on the local news. Reverberations of Clottey’s message is slowly making its way westward to the States. Officially opening today, Mesler/Feuer gallery in New York presents an exhibition entitled “The Displaced” where you can experience many of Clottey’s incredible assemblages, wood installations and plastic sculptures in person. Autre caught up with Clottey during the installation of his current exhibition to discuss his own art history, his politically and socially charged performances, and his ideas of the “New Africa.”
Adriana Pauley: How did your art career start? Did you always know you wanted to become an artist?
Serge Attukwei Clottey: My dad is an artist. I drew and painted at an early age. But I wasn’t sure if I wanted to pursue art as a career. I was more interested in electronics. Growing up in Africa as a child, we got all of these electronics imported from America. I was very interested in how they functioned and in who is behind that creative process. But because my dad is an artist, he thought that I should pursue art. He was going to give me the platform to be successful in that field. So, I got chance to study art in Ghana for four years. Then, I studied in Brazil.
AP: How did you decide you wanted to study in Brazil? Was it a similar culture? Did that influence your art?
SAC: After going through four years in art school, I wanted a way to further my education. I had a scholarship to study in Brazil for three months. I wanted to experience a different place, and how art is shaped differently in that place. Brazil actually changed my entire relationship with art. I became more experimental with materials. In art school, I learned how to paint traditionally. In Brazil, I got a sense of contemporary art. When I came back to Ghana, my approach was totally changed.
AP: Does your interest in electronics come up at some points in your work?
SAC: Yes. Electronics have been a part of my practice from childhood. Now, I combine art and electronics. I work more with performance and installation. I work more with electronic interests. It has given me a new platform to visualize those ideas with materials. It has given me a lot of exposure. It’s very new—combining art and electronics, in Ghana especially.
AP: Has art always been a big part of your life?
SAC: Growing up with my dad, I studied how to paint even before I went to art school. I don’t feel anything special about art, because I grew up in that space. It was a very creative upbringing.
AP: You recently did a performance piece, and you have a performance collective now. What has been the response from the public?
SAC: From the beginning, people were unsure about it. The guys who are in it are not artists actually; they are from different careers. There are a lot of creative people in the community where I was born, but they don’t have the platform to explore that. As an artist, I have that platform. I find a way to bring them together to address issues in our community. Since then, it has been very challenging. The topics we work on are very political. We have very religious subjects. We explore gender identity. Over time, people have become more understanding. We have a lot of presence in the media, in publications. We are trying to address issues such as how the politicians manipulate youth during elections. And how after, they have nothing to offer. We were very critical about that, and it was on TV the whole week before elections. It gave us a lot of publicity. It tells me that it’s possible to create that sort of a platform. I hope we can establish a company which serves as a profit for the group, and for the locals as well.
AP: Would you say, generally, that you would like to give something back to society? To educate them about certain issues?
SAC: I grew up in the community. Ghana has been my inspiration. It makes sense to extend my exposure to the community. The community has been my main collective in exploring my artistic ideas.
AP: In one of the performances you did, you traced the journeys of your family. Your ancestors used to go to the north of Ghana, and come back to the south with different Buddhist techniques. Does that spiritual aspect play into your work?
SAC: It’s played a major role in my work. I wanted to narrate my family’s journey, because we also have a migration background that no one knows about. I’m using the narrative to make a new construction relating to my present work. The idea of continents, of transporting something from one continent to another, is very interesting to me. My family would transport from one town to another, but there is no proper documentation of that history. In my artistic practice, I want to reconstruct that history for my generation. I’m interested in combining my family history in relationship to my new work.
I’m interested in the sea and how it navigates the world together. I’m also interested in finding ways to trade back to the West. All of my materials are imported from Europe or America. The trade relationship changes the value of materials. Africa has come to realize how trade has come to benefit the West. As an artist, I want to find a strategic way to trade back to the West with materials that now benefit Africa.
"Our development needs to be seen. It needs to be shown to the world. We have to acknowledge our past, but we need to develop our present, our future. I’m interested in creating a link between Africa and the people who have been displaced from Africa."
AP: Do you see any parallels between your family’s journeys and your own journeys now?
SAC: I’ve traveled a bit throughout the continent, and I’ve seen how African art is being pursued in different ways. It’s not about people struggling in Africa. I’ve shown my work in Ghana as well as all over the world. There’s a possibility for change that African art is exploring. My family background has been a guide in my artistic journey. I see how powerful my ancestors were trading on the coast. That is the spiritual aspect that has been guiding me on my journey.
AP: You use a lot of plastic, which is very important in the United States. It is important in Africa, too, but for other reasons. Do you address that issue?
SAC: I try to address where my materials come from, and how that changes the value of those materials. There is a big difference between a plastic that is made to be presentable and a plastic that is being dumped somewhere.
AP: How do you gather that material?
SAC: We collect them on the coastal beaches, as well as at dump sites. In Ghana, because of the volume, there is no space to consume them. They find ways to dump them. We don’t have proper recycling structures. You end up seeing them on the streets and in the ocean. For me, the material plays a very significant role in my work. I take care in picking out and repurposing the plastic that has been discarded.
AP: What about colors? I know you use a lot of yellow. Do colors have a certain meaning in your work?
SAC: The dominant color is yellow because yellow is used for transporting oil. Looking at yellow in Ghana, it’s in our flag to symbolize wealth. But I want to change that. It shouldn’t be about the “New Africa.” What can we generate from this plastic? It has become part of our life. We need that to survive. Instead of getting it out, we can use them. We can’t just store them; need to take care of the environment. Once I put them together, I can build houses. We need to innovate new ways of dealing with this.
AP: Can you explain your concept of “Afrogallonism?”
SAC: Afrogallonism is a word I made up after working with this plastic for fifteen years. Over time, it has become my second skin. Every time I see a gallon, I get inspired. I realized that the top of it looks like a mask. Afrogallonism is the new Africa, the future of Africa. We have traditional masks, but this is the mask of our time. This is a relevant mask that brings up issues of water and environment. It’s a movement that I started. I want to find ways to inspire people to work with plastic. Afrogallonism is a word that came up after realizing how much time I have spent working with this material.
AP: What would you like your American audience to take away from your exhibition?
SAC: The displays are about migration and how people have been displaced all over the world. Coming from Africa, I’m interested in bringing that kind of connection—the relationship of humans and materials. I’m interested in how migration has displaced everyone. I want the audience to see that this is a New Africa. This is Africa in the 21st century. This is what we are going through. Our development needs to be seen. It needs to be shown to the world. We have to acknowledge our past, but we need to develop our present, our future. I’m interested in creating a link between Africa and the people who have been displaced from Africa. As this material comes to America, I hope to create that link.
AP: Do you have any upcoming shows or performances planned?
SAC: Right after this exhibition, I have a performance in Ghana, just before the next election. I’m very critical. When it comes to politics, people have loud voices, but they are not heard. As an artist, together with my collective, we perform in public space. We hit the matter hard. We want to use our exposure to address that relevant issue.
Serge Attukwei Clottey's "Displaced" is on view now through November 22 at Mesler/Feuer Gallery, 319 Grand Street, 2nd Floor New York, NY. Follow Afrogallonism here. intro text by Oliver Maxwell Kupper. Interview and photographs by Adriana Pauly. Follow Autre on Instagram: @AUTREMAGAZINE