Photographer: Claire Dorn. Courtesy of the artist and Perrotin.
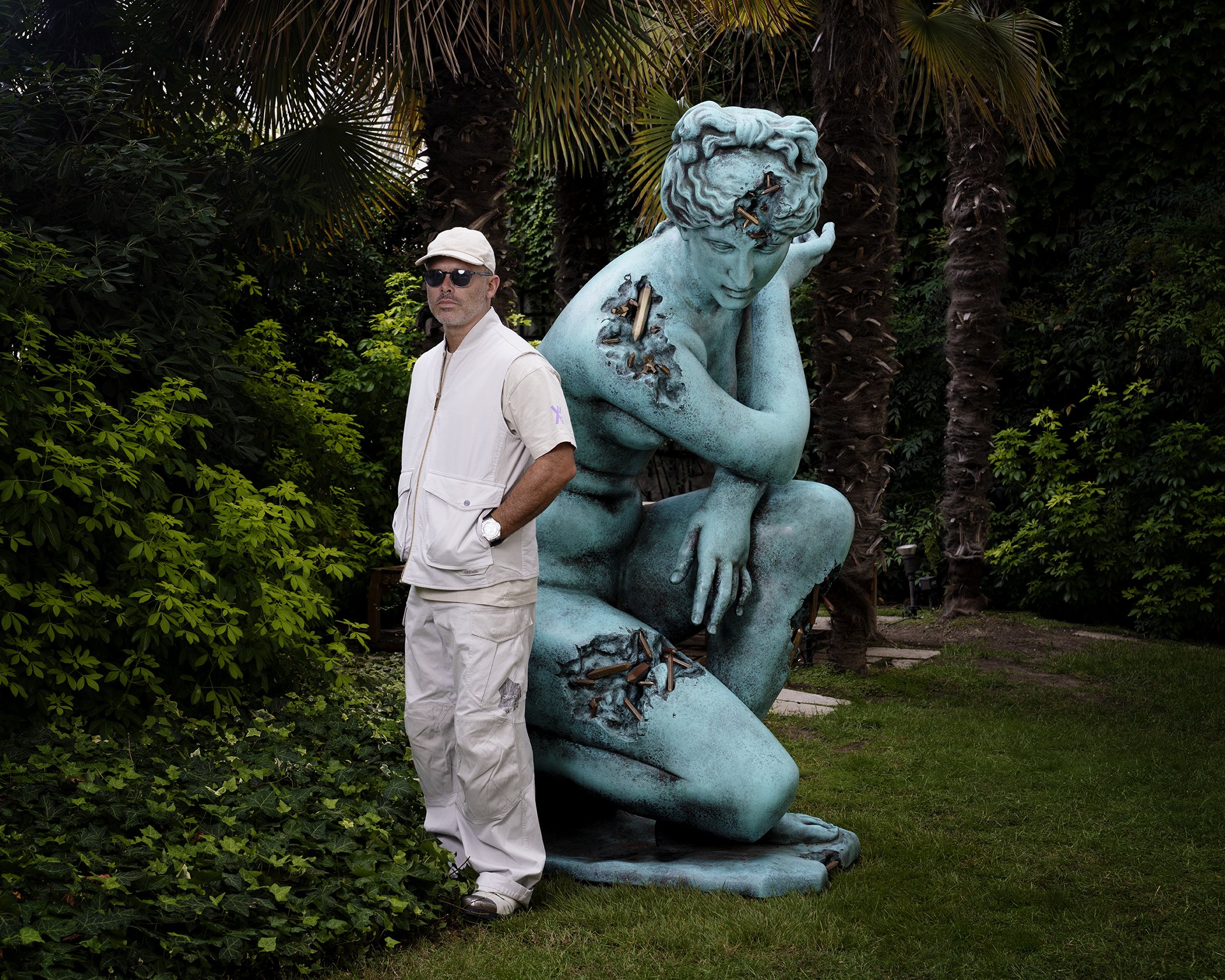
In a globalized world, pop culture transcends dialect to create a language accessible to all. Daniel Arsham’s work taps into this reservoir of collective symbols while cheekily disconnecting them from their cultural niches, sending R2D2 back in time to erode and replacing it with a fresh Venus de Milo. Patrick Moore, the director of the Andy Warhol Museum and an expert judge of the weight our common cultural relics hold, has previously examined Arsham’s work through a lens tinted by Warhol’s campy visual commentary. While Warhol crafted the thrones of monolithic cultural figures, however, Arsham’s work presents the modern deities of culture and especially Americana as decaying relics. Despite this alternative view, his work maintains a celebratory and even reverent attitude toward its subject matter, which has landed him partnerships with Star Wars and Pokémon alongside the Merce Cunningham Dance Company and Perrotin, his gallery of twenty years. This fall, the artist celebrates this two decade partnership with dual exhibitions across Perrotin New York (through October 14) and Paris (through October 7). In honor of this anniversary, Moore and Arsham come together in conversation to explore the bridge between commercialism and fine art where Arsham and Warhol have built their practices.
DANIEL ARSHAM: When I did the press preview in Paris, I was asked what I thought about your essay in comparison to Warhol. Certainly, for me, it's a flattering comparison, but it gets to the heart of people feeling sometimes like what I'm doing is this very novel approach. It's almost like people forgot that Warhol was doing this 40 years ago. I think I told you, Patrick, about the story when I did the first collaboration with Adidas. I was having a conversation with a collector of mine who was like, how are you gonna allow this brand to use your work to sell sneakers? And I said, it's the opposite. I'm using them for their reach and the funding that they're gonna put towards this crazy project that I wanna do.
PATRICK MOORE: I think that people not only forget about how earth-shattering it was when Warhol was first blurring the lines between the commercial world and the fine art world, but they also forget that Warhol had been largely dismissed at the end of his career. For a large part, I think that there was this backlash at his exploration of the commercial world and of making money as part of his practice. Do you think that still exists in the art world? Or has it become an accepted practice?
ARSHAM: I don't know if it's more accepted, but maybe the artists who are doing it feel more comfortable around it. I'm thinking art of artists like George Condo or Tom Sachs who were already kind of integrating those sorts of elements within their own work, and it didn't matter whether the brand was directly involved with them or not. The context of those brands in their work already existed. So in some cases it's a benefit to maybe have the brand supporting that.
But really, what's the difference between a brand and a collector? The collector is purchasing or supporting. So much of my audience are not the traditional art world audience. And every time that I do an exhibition, when I post about he show, people always ask if they need tickets to come to the gallery. And I'm like, guys, this is the greatest thing ever. You can go to any art gallery and it is 100% free. Here in New York, it's like a huge free museum, and the collectors are the ones who pay for the audience to be able to see it.
MOORE: I was so glad that you and Perrotin asked me to think about this because as I mentioned in the essay, I had been thinking so much about you, and it was really seeing your work in that different setting that you described at Tiffany's in New York that started this. For you, how is it when you walk into that store and you see your work in that context? Does it feel fundamentally different than seeing it in your studio or in the gallery?
ARSHAM: In some ways it feels more natural in that location than seeing it in the gallery. I feel like the gallery, maybe it's a more minimal environment, but it's much more directly about the monetary transaction with the work. And at Tiffany, it's just there for people's pleasure or their inquisitiveness or curiosity. So it was like, the jewelry that was worn in, Breakfast at Tiffany's and other famous pieces that have been worn either in film or on the red carpet and outside of the exhibition. I had done work with Tiffany in the past, and they wanted a large work to be out there to kind of announce what was inside.
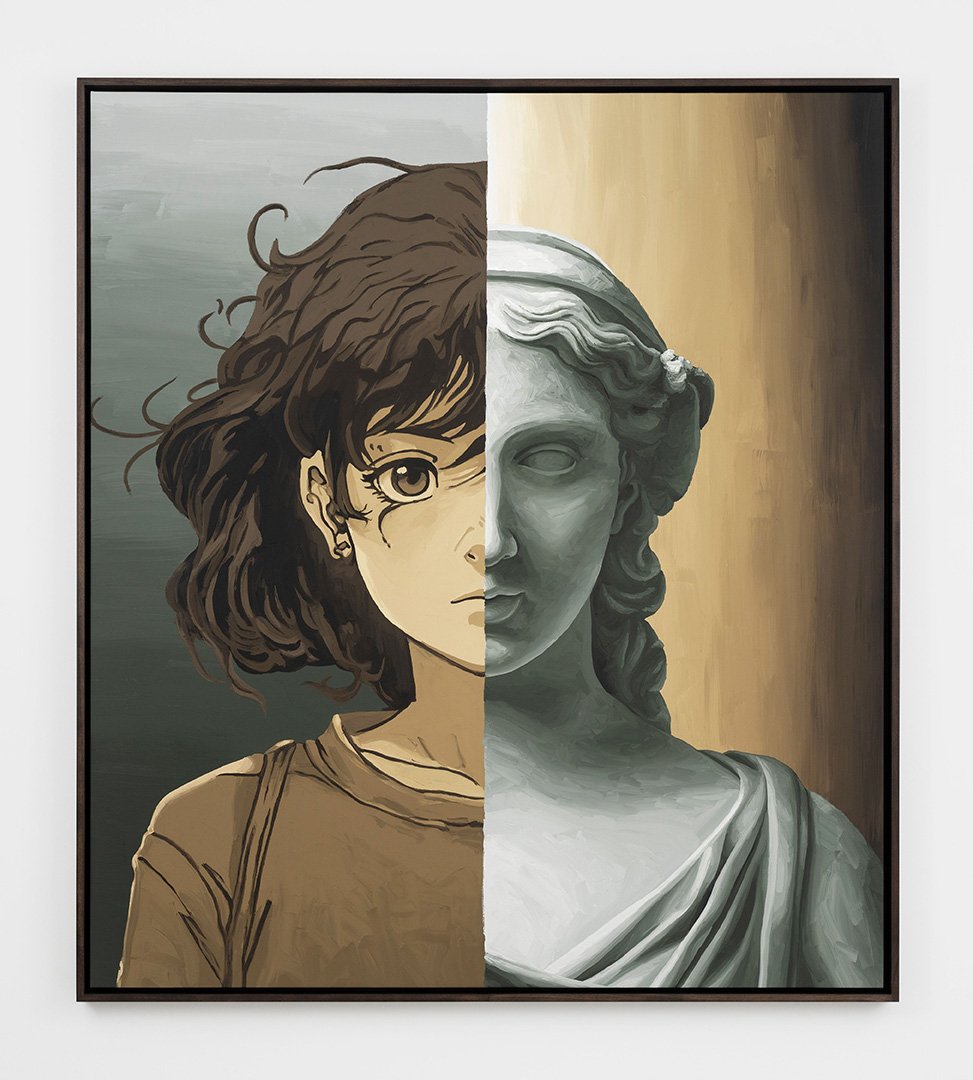
Fractured Idols I , 2023.
Acrylic on canvas. Framed: 91 1/2 x 105 1/2
inch. Photographer: Claire Dorn. Courtesy of
the artist and Perrotin.
MOORE: In my essay about you, I also mentioned this idea of you ruining things to make them more precious or to help us see them new again. What did you think about that idea of ruining things?
ARSHAM: When I first started with that body of work, it was really about this idea of aging them, causing them to appear as if they're from a different era. And so much of the work that I've done from the beginning was always about time dislocation, where we're looking at a painting or an image or a story or a sculpture, and we don't quite know when it is from. Sometimes in the depiction of a painting, we see a landscape and there are these architectural structures within it, but it looks like maybe something ancient or something ultra-futuristic, and we don't really know when we are. And so the idea of decay in the works was really about causing the work to appear as if it's in a state of erosion, like it might be in 10,000 years. And the materiality of it is really important for the further understanding of what the object can be. Like, the crystals tell us something about the idea that a trompe-l’œil version of that would not. Like if I just took a radio, let's say, and I painted it to look old, and maybe the quality of it was sort of visually similar, the knowledge that it's actually made of crystal has this other sort of visceral truth quality about it. It's also very difficult to understand how they're made, which is a magic that I think artists often employ. You just can't understand the object.
MOORE: When we look at your work, we see an object, but there's actually something that you're hiding underneath that object. In almost everything that you do, it seems like I'm seeing something, but you’re not letting me see what this is really about.
ARSHAM: I guess that's one way to look at it. The other way is that you're seeing something in the objects, and this is part of the reason why I use things that are very familiar to almost everyone. No matter where they are in the world, it allows them an entrance point into the work. Like, I feel like I know that thing. I'm in. Once you get there, things become more complicated. When is this thing from, why is this wall moving? That use of the everyday object as an entrance point into my work has been consistent and super important for me.
Holiday Inn: Study for Falling Clock, 2023.
Graphite on paper. 10 1/2 x 7 1/4 inch. Graphite
on paper. 8 7/8 x 6 1/8 inch. Photographer:
Guillaume Ziccarelli. Courtesy of the artist and Perrotin.
MOORE: I want to know a little bit more about how and why you draw. Do you draw every day? Is it a part of your practice every day? Is it something that's associated with projects?
ARSHAM: It's for different uses. I use it as a way to prepare. I use it as a way to think. Sometimes concentrating on an object or an idea in drawing, when you're not really thinking about language, has a different way of telling you something about it or understanding something about it. And then sometimes drawings are really just like notation. I've been either making drawings in hotels for years. I always take the stationary with me. Some of my favorite ones are like the Holiday Inn from Arkansas or something like that, where it's a really bad graphic. That contrasts with the drawing that I'm doing of an eroded Greek figure or something like that.
MOORE: I had a more glamorous fantasy of you than the Holiday Inn. I was thinking of you in some glamorous hotel in Tokyo at 3:00 AM, jet-lagged out of your mind, like, I'm gonna start drawing. Holiday Inn never occurred to me.
ARSHAM: When I toured with Merce Cunningham, the accommodations were not luxury. It was wherever he could put up the entire dance company. But [in the exhibit] there are drawings from Gritti Palace in Venice or the Amman in Tokyo. It's the whole range.
MOORE: I saw a couple paintings that you were working on in your studio, and I was really, really drawn to them. One thing I was drawn to was the paint itself. I was wondering if you could talk a little bit about the paint, the matte quality of the paint, the palette that you're working with.
ARSHAM: I'm colorblind, and I think it has always made it very challenging for me to mix and match paint. If I'm working one day, and then I come back the next day, I always found it ultra frustrating to try to remake a color that I had mixed to match something that was already on the canvas. So, I had been working with this company, Golden Paints, to basically make me a complete gradient in the four colors that I wanted to use. They kept sending the sample, and I would say “Add more pigment”. I think that quality that you're describing is this feeling in the paint that it's just so lush and loaded with pigment. It's got like 20 times the amount of pigment that's in a commercial paint.
MOORE: Well, here's a big difference between you and Warhol. I think Andy used the cheapest possible paint he could find (laughs). Let's talk a little bit more about the paintings, because they are such an odd amalgam and it makes them really interesting. What I responded to was this idea of nostalgia and Americana, but I'd love to hear you talk about the paintings and what you were thinking about specifically when you selected those objects, those scenes that you create.
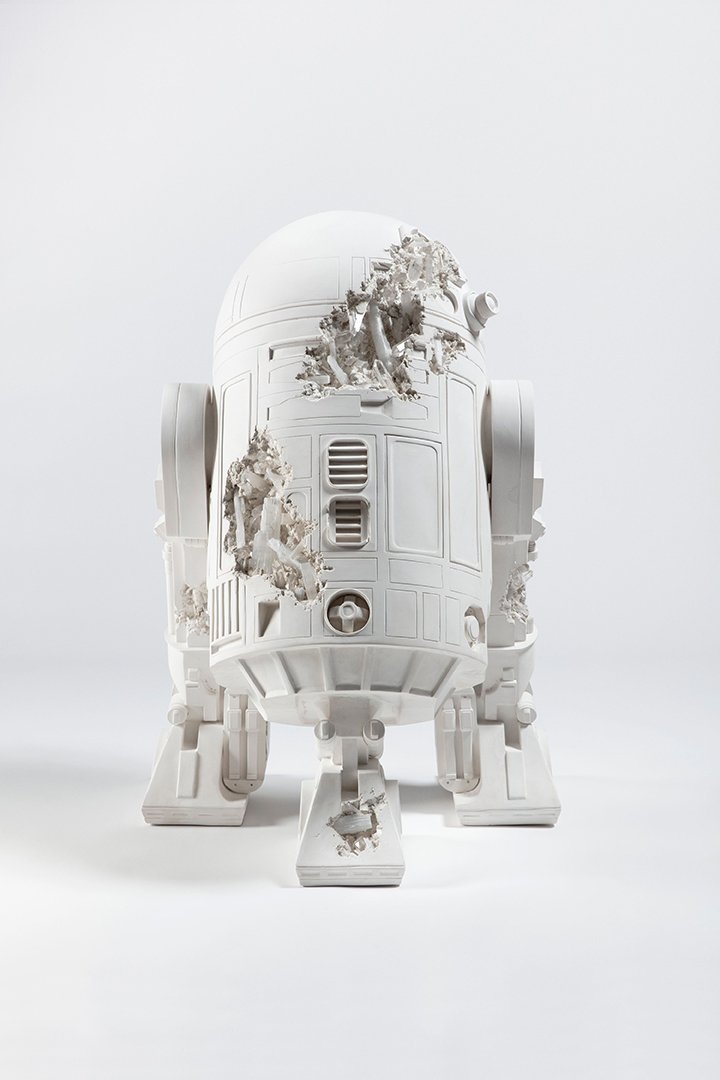
ARSHAM: I had been working for the past couple of years with the Pokémon Company in Japan, and I made a number of sculptures based on some of the Pokémon characters. And we also worked on an animation together that I insisted was hand-drawn. I did a couple paintings at the time that were like a single cell study. This exhibition has a number of works in it that use that anime or manga-type language in them. I'm mocking up most of my paintings from multiple different images–I'm basically doing a collage in Photoshop, and then I'm using that as a reference for the painting. So I'm throwing in references to old Air Jordan ads or vintage Porsche ads. There's cars in them, there's sneakers, there's the BMX bike from the movie ET. And it's all of these Easter eggs that encompass my world. And in the exhibition there, those works also exist in sculpture. So you might see like an R2D2 in a painting in silhouette. And then in the show you're seeing the actual sculpture of it.
MOORE: Star Wars is a particular focus right now. Was that like a touchstone for you growing up? Does it have a kind of magic resonance for you?
ARSHAM: It's really one of the first movies that I can remember seeing in the cinema with my family. I was probably five, I guess it would've been Empire Strikes Back, and kind of just like something that was always been around. When I was a kid and I would stay home sick from school, there was a VHS that my father had recorded, one of the Star Wars, but he had recorded it from television, so it had all the commercials in it out as well. And so up until I was in high school, I'd be watching commercials from like the eighties mixed in with Star Wars. I wish I still had that VHS ‘cause it probably encompasses like everything that I'm interested in. You know, today I cook advertisements, um, you know, a Super Bowl commercial or like n b a playoffs and the Nike ad and you know, car ad and then Star Wars in between.
MOORE: Star Wars is so fascinating. Business is so much a part of your work – how do you go about working with a franchise like that? How does something like that happen?
ARSHAM: I had been speaking with some people from Lucasfilm in advance of the project in Monaco with Louis Hamilton. George Lucas is a huge F1 fan, and I think he'd been to every Monaco Grand Prix since the seventies. And he was there at the event with his wife [Mellody Hobson], and she says to me, I think we own some of your work. I was like, what? George Lucas has some of my work in his house? What is this? And so I'm like, which work is it? Like, where did you get it from? And she's like, Usher gave it to us as a gift. It was a work from about 15 years ago, a 35 millimeter movie camera that I had cast in volcanic ash. I don't think she knew who the artist was or anything, she just recognized it because of the similarity with the work that I had done for Louis. And so I told her, “by the way, I'm speaking with Lucasfilm about this thing.” And she connected me with the right people. And that's sort of how it came about.
MOORE: Well, it was meant to be then.
Daniel Arsham 20 Years will be on view at Perrotin New York until October 14, and Perrotin Paris until October 7.
R2 - D2TM: Quartz CrystallizedFigure , 2023.
Quartz, Selenite, Hydrostone. 48 x 42 1/16 x
42 1/16 inch. Photographer: Guillaume
Ziccarelli. Courtesy Perrotin. © & TM
Lucasfilm Ltd. © 2023 Daniel Arsham, Inc.