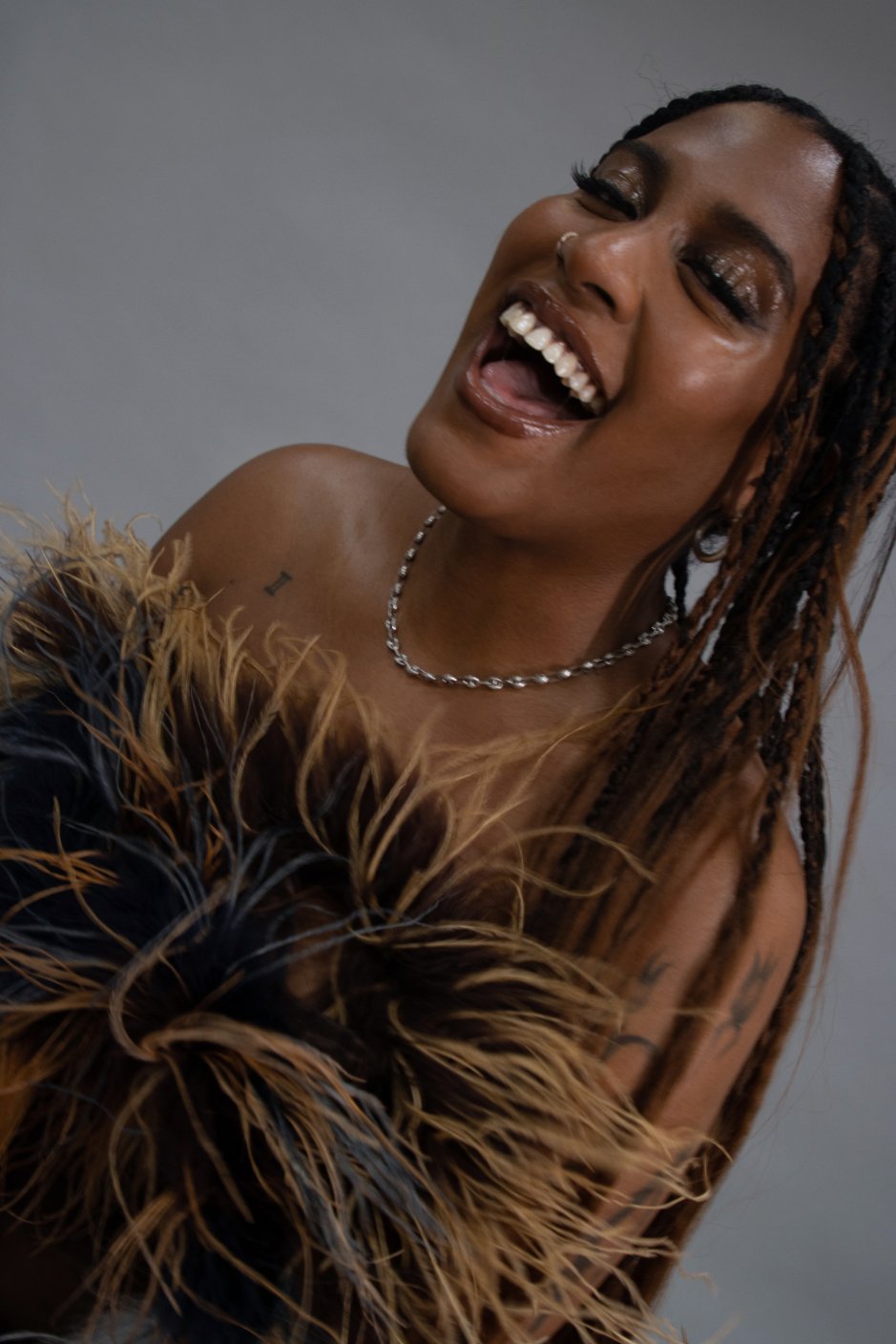
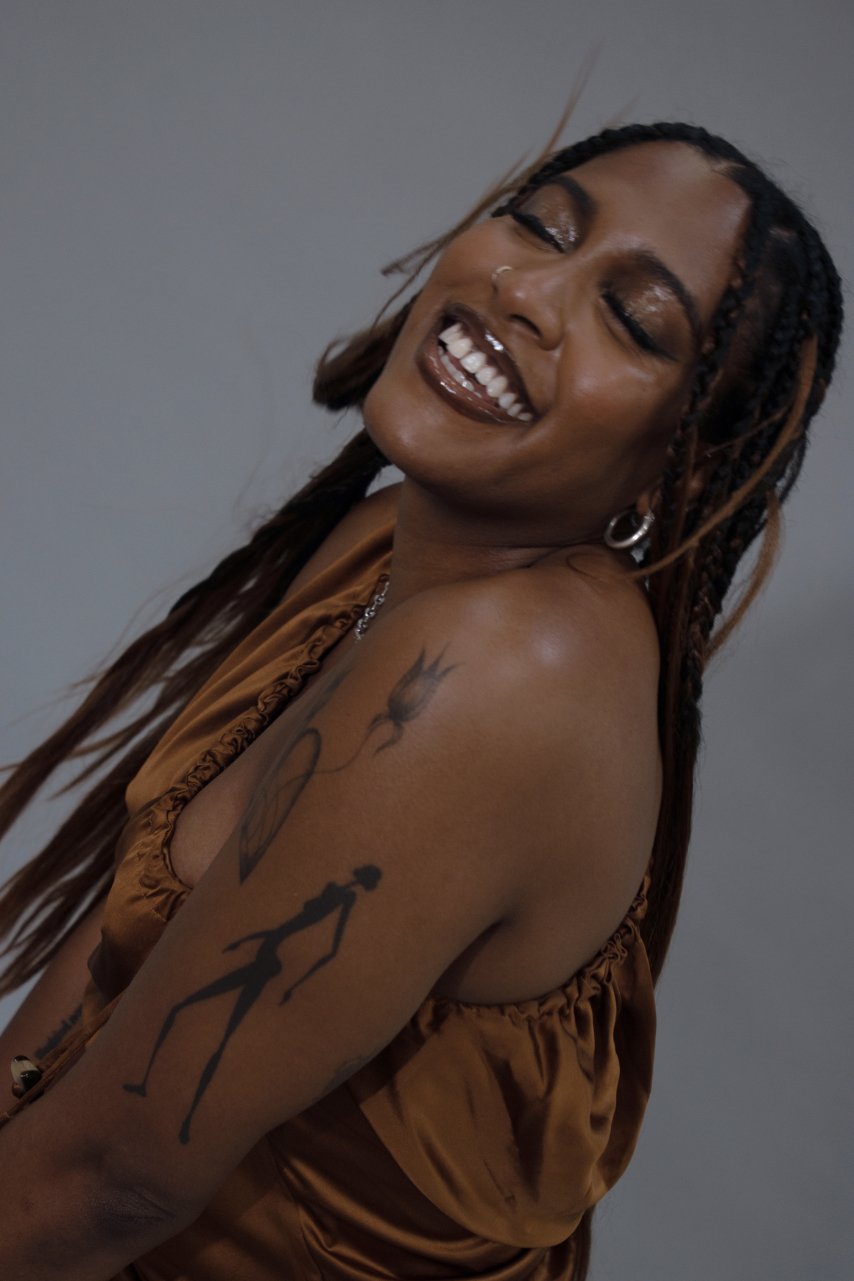
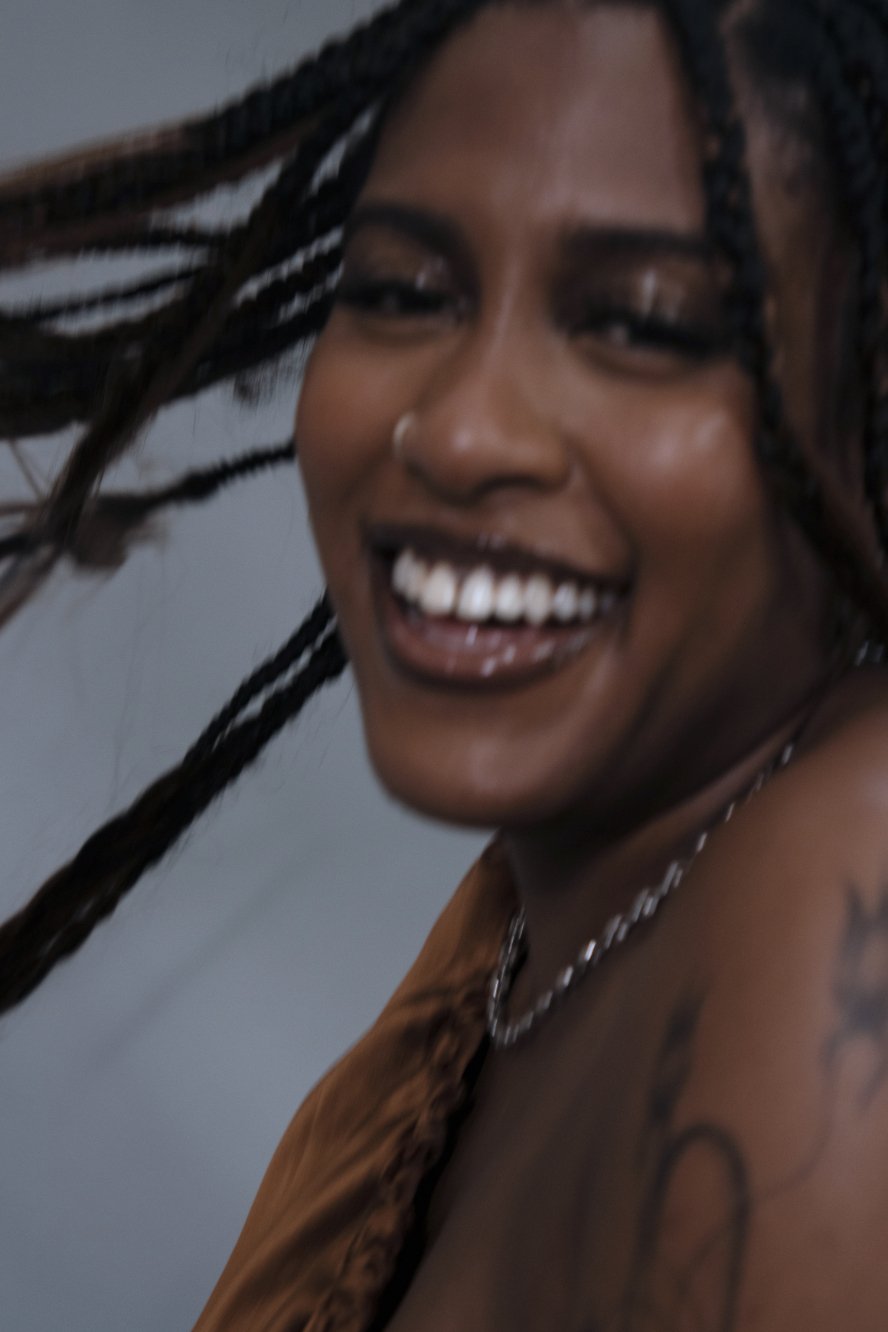
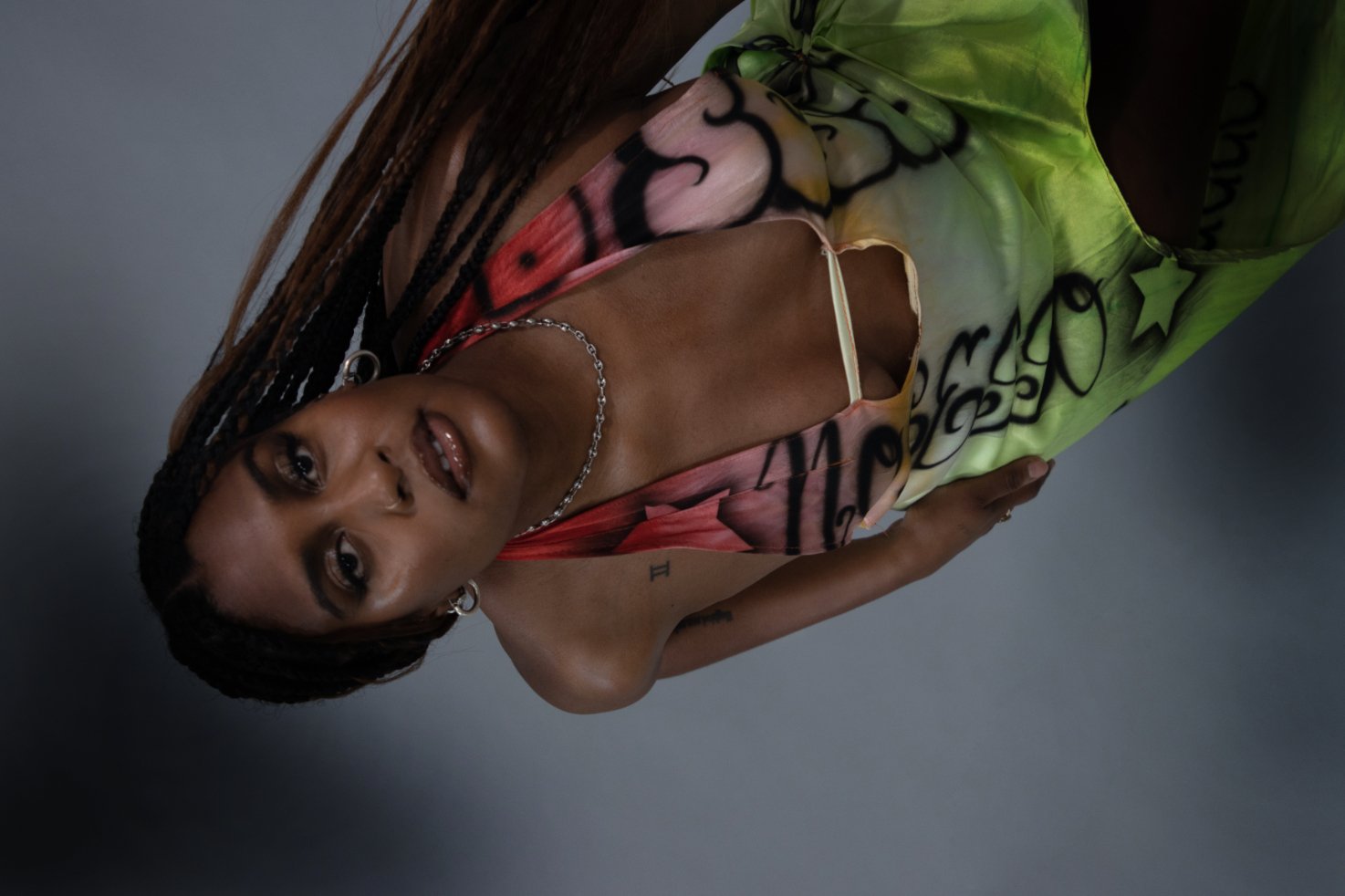
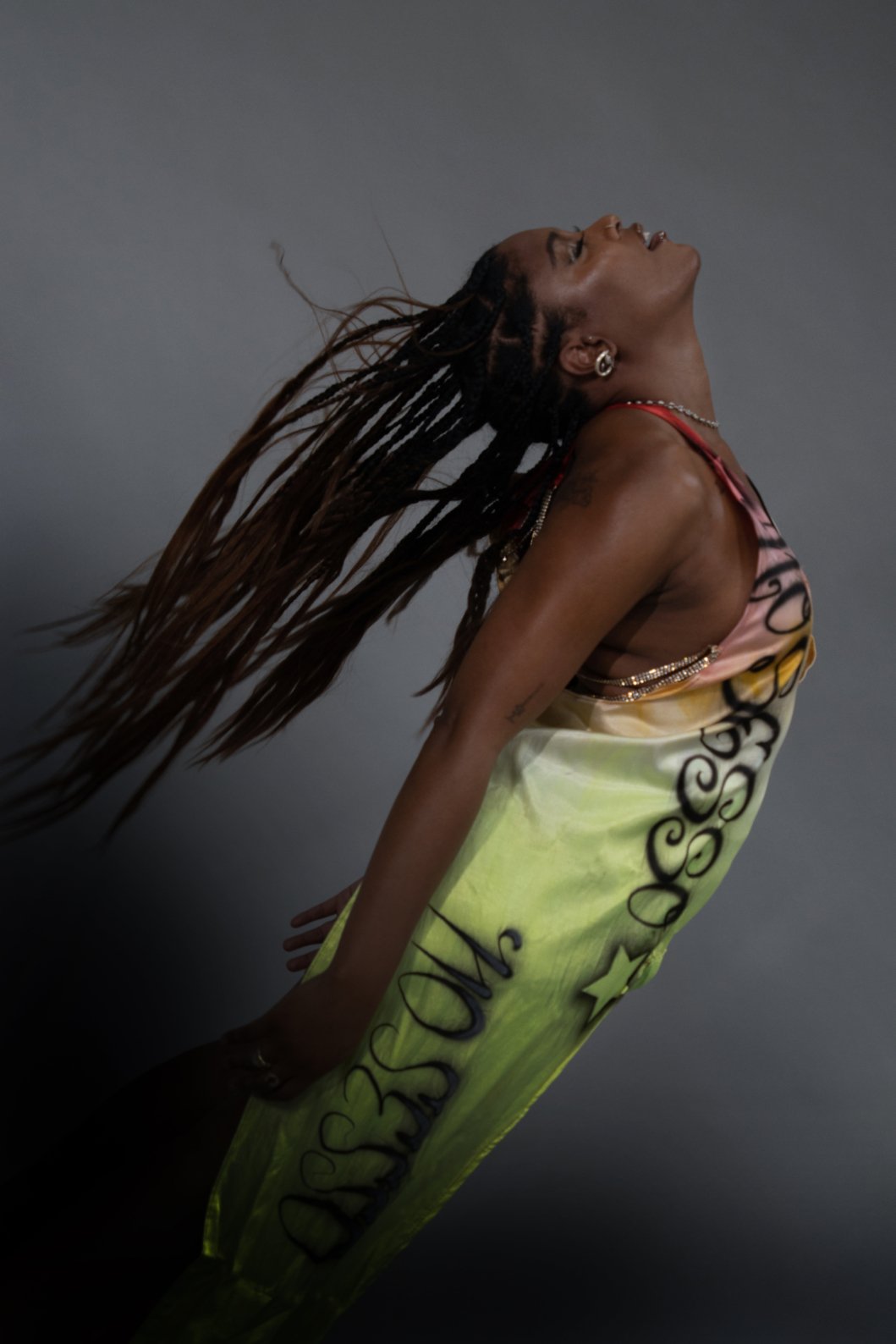
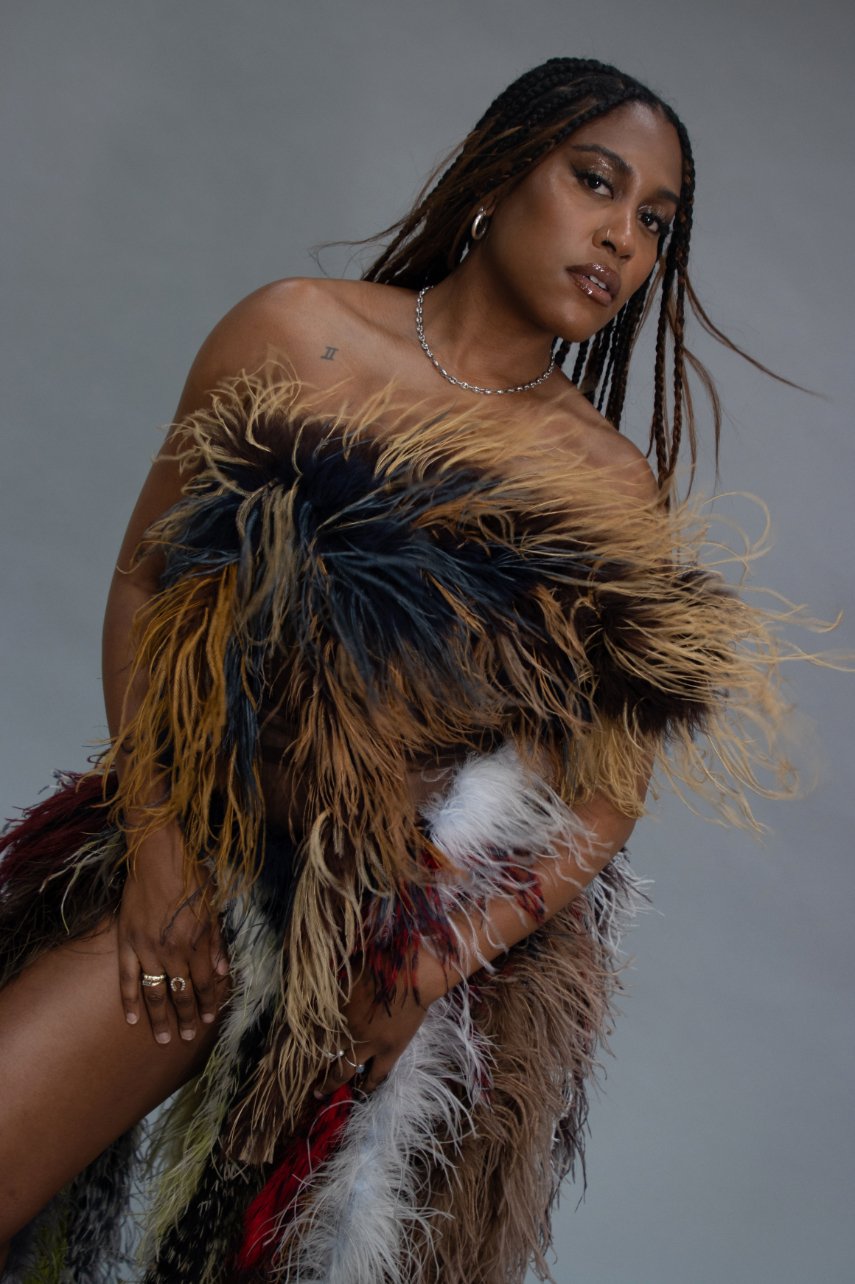
Alison Blickle
Night Fate, 2025
courtesy the artist and Kravets Wehby Gallery
interview by Charlie Kolbrener
In Alison Blickle’s work, viewers are invited to witness a glimpse of a world just as realized off the canvas as it is on it. The figures at the heart of her painting—sometimes based on elaborate photoshoots, sometimes an amalgam of disparate body parts from various sources—are characters who signal larger narratives reflecting our modern world, or concocted visions that live outside of time. Her latest collection, Future Ruins, on view at the Kravets Wehby Gallery, invites attendees to inspect a future that infuses a nostalgic melancholy for nature with a glimmer of the beauty still accessible in her perhaps pessimistic view of what lies ahead.
Blickle has effectively been painting her whole life, but went on to study Political Economy when plagued with the feeling that “it felt too impractical to pursue as a career.” After working for Diane Feinstein for six months, her realization that “whatever your job is is what your life is” would send her back to get her MFA at Hunter College and embark on the creative path that sees her work on display in New York City now, over a decade later. As we prepare to discuss her new collection, she reflects to me how she first made the leap into pursuing painting: “I have to pursue what I know fulfills me and what I love.”
CHARLIE KOLBRENER: The process for creating this collection differed a bit from your work over the past few years. Can you tell me a bit about how you were producing work previously?
ALISON BLICKLE: I didn’t do it for this body of work, but for the past five or six years, I would put on big photoshoots to get reference images for the paintings. And they ended up getting pretty elaborate. I did a shoot at Jeffrey Deitch’s house in LA, in the Hollywood Hills. I would find interesting locations and have mostly art world friends helping set up lights, build sets, and everything. And that was something I’d never done before. I’d been painting for so long, and I found ways to challenge myself with it and to evolve with it. So, it was fun while I was doing these shoots to push myself into a totally different thing. And painting is totally solo, so having to collaborate and direct people and everything, it was fun.
Alison Blickle
Snow Hike, 2025
courtesy the artist and Kravets Wehby Gallery
Alison Blickle
Hilltop Meadow Experience, 2025
courtesy the artist and Kravets Wehby Gallery
KOLBRENER: And then what was the process of taking these images and converting them to painting?
BLICKLE: There was never one photo where it’s like, I’m gonna paint this. It was always chopped up and combined from other ones. I would collage in architectural elements or fake nature elements or weird objects or neons hovering around. You can recognize the people for sure. It’s true to what they look like, but I did a lot of manipulation from the photo that I took to what I ended up using as the reference for the painting.
KOLBRENER: How did the process differ as you approached this collection?
BLICKLE: I’m an art history nerd and I love classical painting, where they’re painting myths with very dynamic groups of figures. I love that tradition so much that I wanted to carry it through to the present day reflecting modern life. I was making a lot of these group paintings with life-size people that were very detailed and maximalist, but I think I’d sort of maxed out on the maximalism. This time, I wanted to make a body of work completely on my own.
Every body of work basically has a narrative underpinning and when I was doing those big group paintings, I would choose an ancient myth that has a powerful female archetype, or goddess in it. Then I would set that character or story in the modern day and connect it to things that are happening now. I love how mythologies have a universality and timeless wisdom that feels comforting, like a guide for modern life.
This time, I wanted to simplify the paintings and try something different. Instead of using the past to help understand the present day, I did more of a sci-fi vibe. The story behind these is that they’re set in a dystopian future where nature doesn’t exist anymore the way it does today, but people still have that longing to connect with something larger than themselves in a spiritual way. The only way that people can do that in this world is in a virtual reality experience, and they go into that as an avatar of themselves. So these paintings are of avatars in these artificial digital environments, hoping to have some sort of feeling of transcendence or connection to something larger than themselves. But it’s falling short and that’s why some of the figures are crying. I’m trying to blur the line between, are they feeling sad because it’s not what they were hoping would happen? or are they partly overcome by actually seeing a space like this for the first time?
KOLBRENER: How are the subjects produced for this series where you’re not relying on actual models and shoots?
BLICKLE: They’re almost like Franken-people, where none of them are an image of a single person. The heads are from different places, they’re all just cobbled together from different sources. And same thing with the environments that they’re in.
I also think about AI a lot. My previous show was a sort of prayer to this particular Roman deity who oversees periods of transformation to guide humanity into this transition with AI, not knowing what direction it’s going to go for us. I’ve been really into AI for years now, from a place of fear. I mean, you can already buy AI robots that look really human, you can buy an AI robot girlfriend. So, assuming that trajectory continues, at some point, there’s going to be AI robots that are living amongst us. And if they do develop some level of consciousness, something that they might be interested in is what it would have felt like to experience nature in this way. So, these could be human avatars, or they could be robots going through this experience.
Alison Blickle
Mask, 2025
courtesy the artist and Kravets Wehby Gallery
There are moments in all of the paintings where I used an AI prompt to create a little section. For example, I wanted to put a weird sun in the sky. That was generated by AI. All of the paintings have a little section that was generated by AI, and I think it sort of conceptually works with the paintings. There’s still a weird awkwardness of AI that made sense with these figures being in a curated digital world.
KOLBRENER: In this collection—or in your work more broadly—what do you look to outside of art to take inspiration?
BLICKLE: Definitely movies, David Lynch is a big inspiration. The paintings in this show that have the duos in them, I was thinking about Mulholland Drive and the doppelganger, or the alter ego. In this piece, where the arms are crossing, the fabric is sort of blending into each other, and it's hard to tell where one starts and the other ends. I love David Lynch's dark surrealism, but his colors are so beautiful.
Alison Blickle
Day Trip, 2025
courtesy the artist and Kravets Wehby Gallery
KOLBRENER: How do you feel your art and the themes within it more generally have evolved since you started?
BLICKLE: It’s a good question. One through line has been that I always—on some level—feel like the figures are a stand in for myself to get to do certain things that I don’t do in my regular life. So, it’s a way of living vicariously through my paintings.
In terms of evolving, this is my favorite work that I’ve ever made. I’ve been making paintings for so long now, and this is starting to circle back to older work that I made, where these figures are having more of an internal experience. They feel quieter, more contemplative, and a little bit isolated. There’s a melancholy and beauty to them, which reflects modern life. When I started doing these elaborate photoshoots, the figures in them were very performative. I was working with ideas about social media a lot, and how that changes how we think about ourselves. So, the characters looked like they were on stage, and they wanted to be looked at. I explored those externalized, ‘look-at-me’ performative scenes long enough. And now, I’ve been doing a lot more introspection, so I wanted the paintings to circle back. They don’t visually look the same, but they have that same similar quietness. The characters are having an internal experience that you just happen to witness.
Future Ruins is on view through October 4 at the Kravets Wehby Gallery 521 West 21st Street, Ground floor, New York
Alison Blickle
Ladies Night, 2025
courtesy the artist and Kravets Wehby Gallery