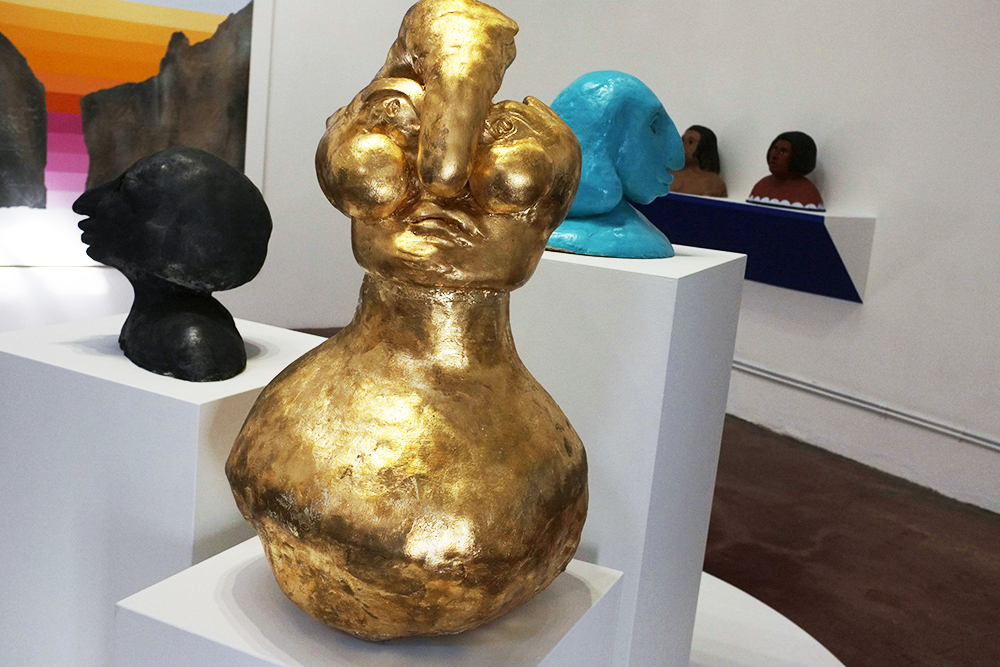
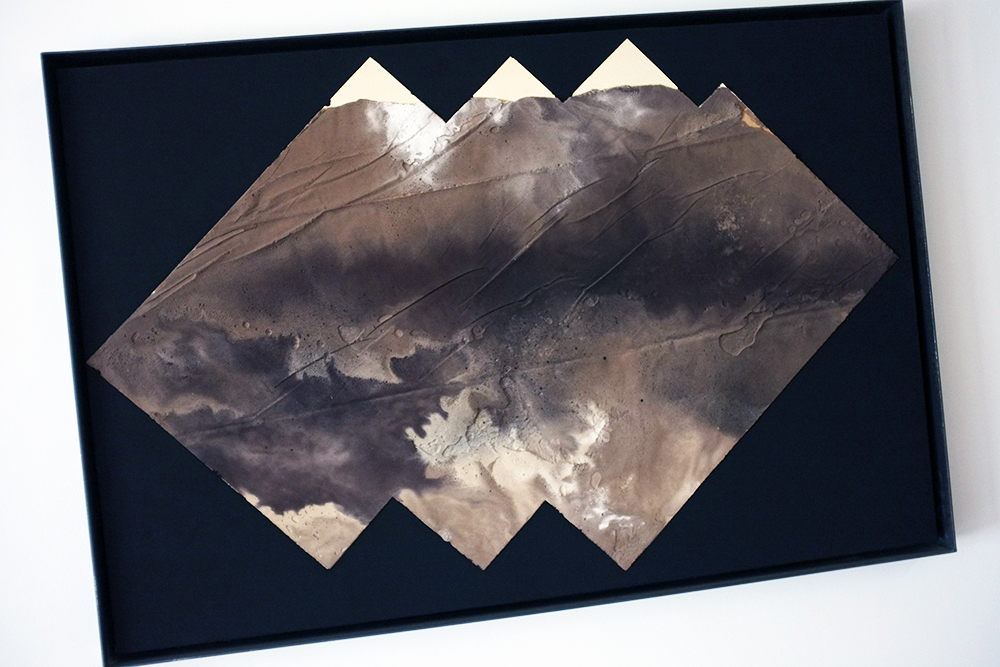
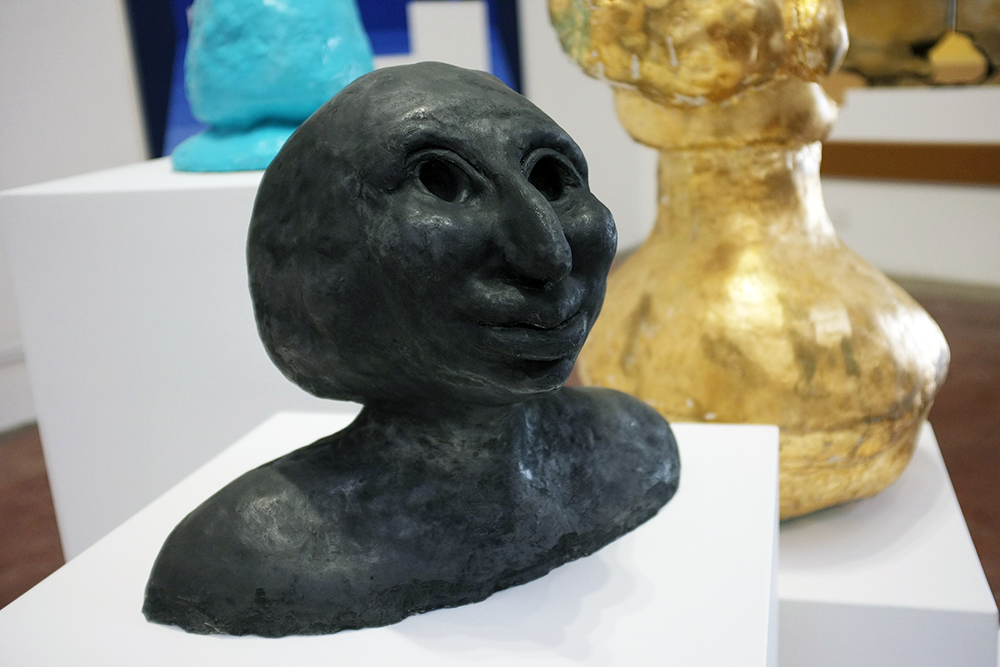
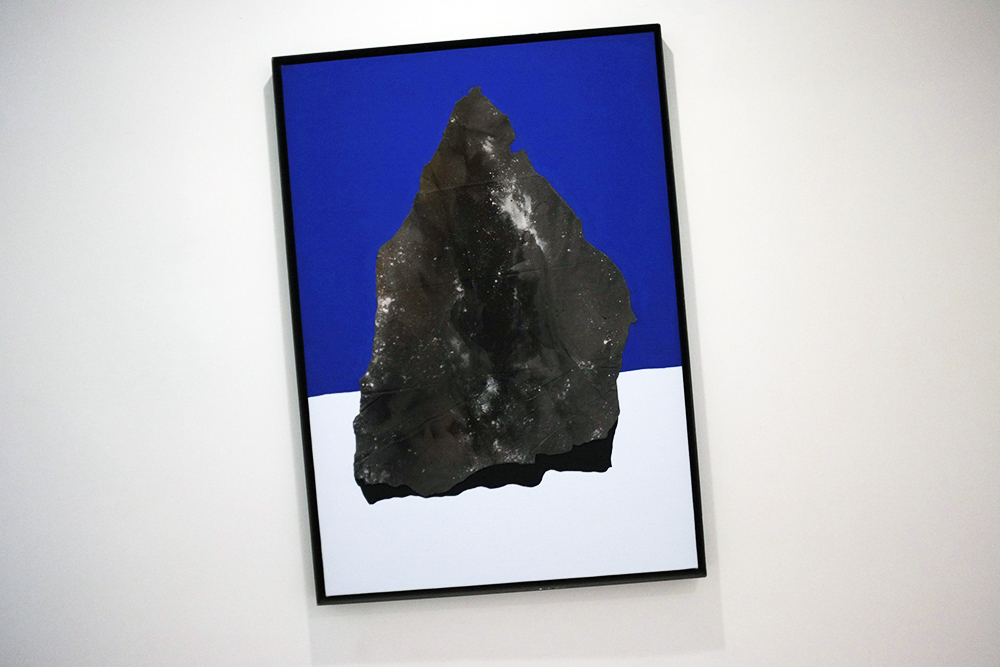
Louise Frances Smith
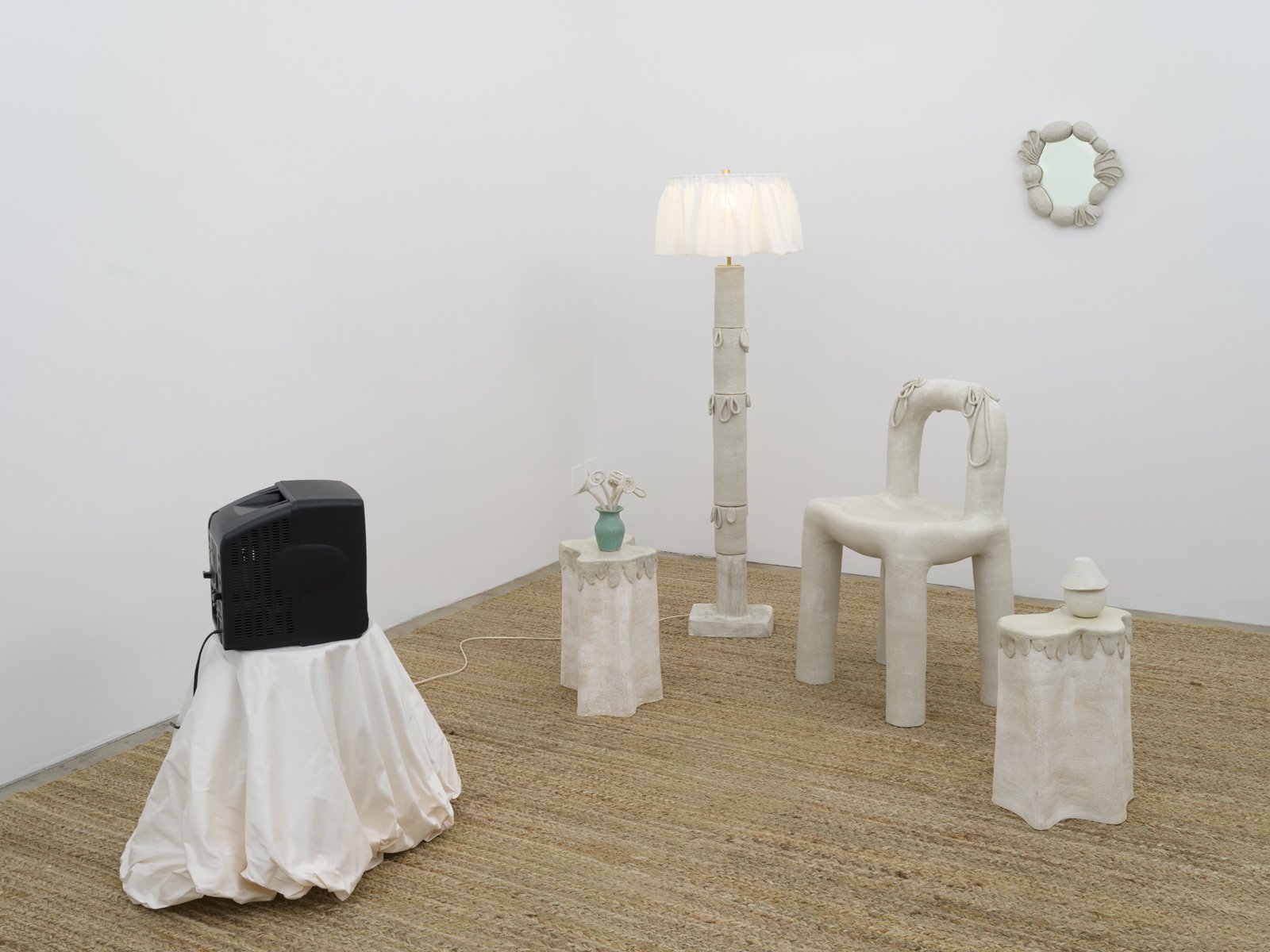
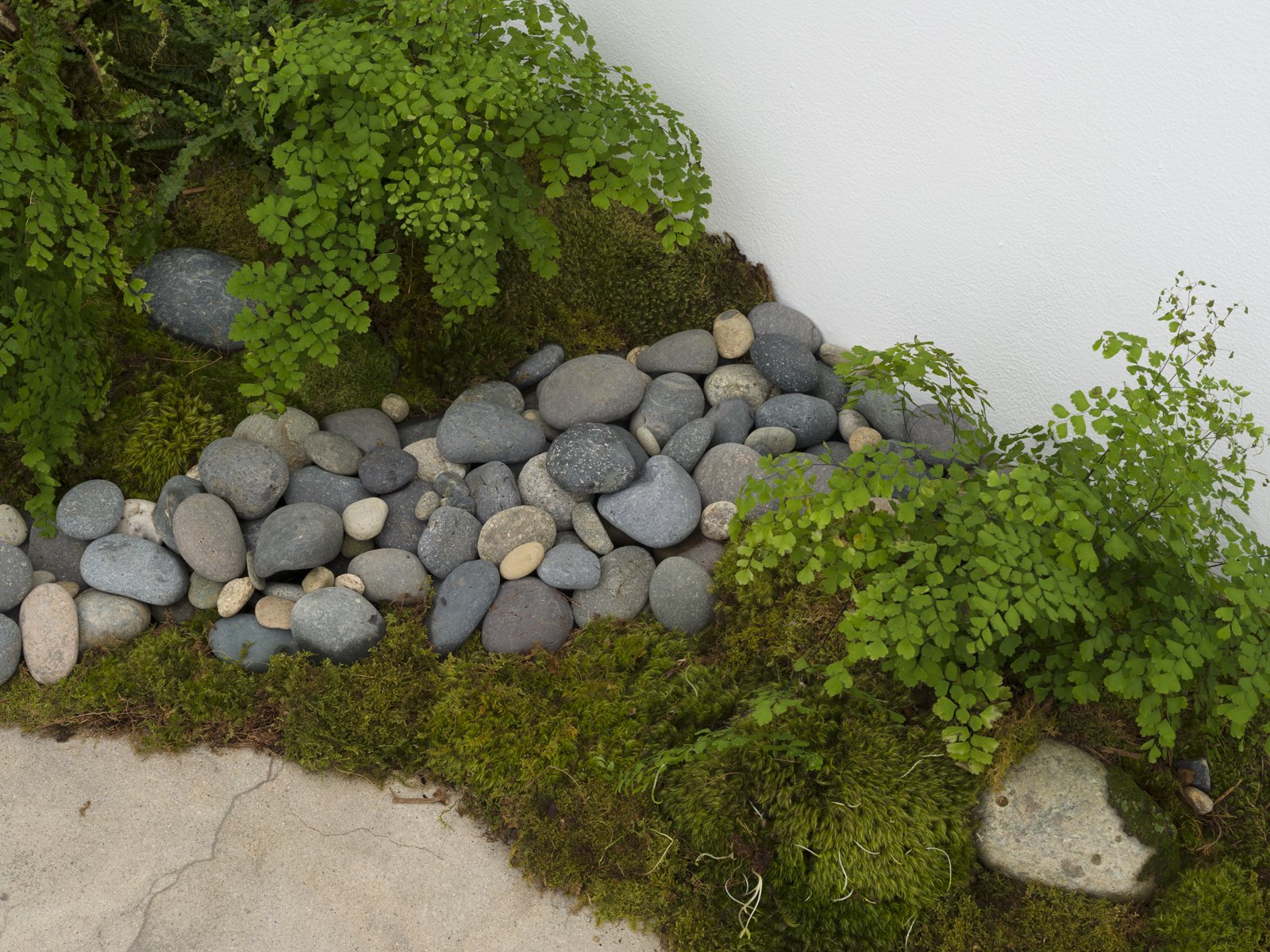
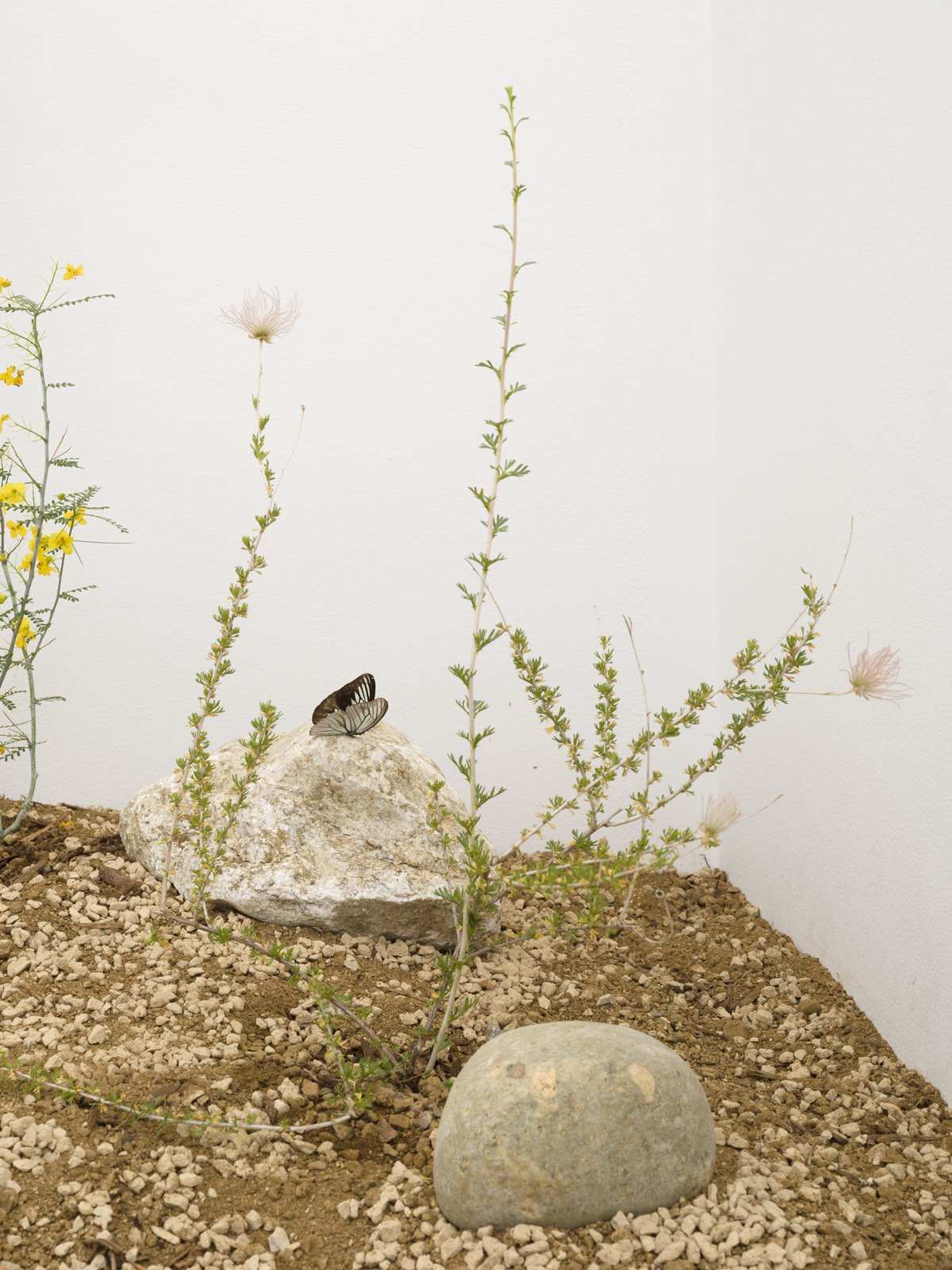
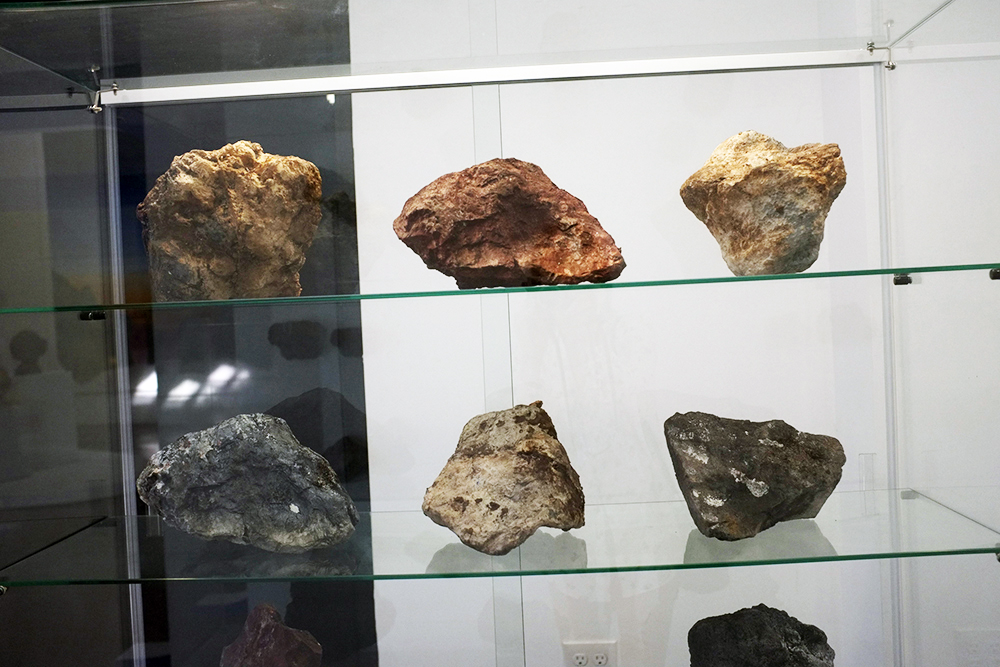
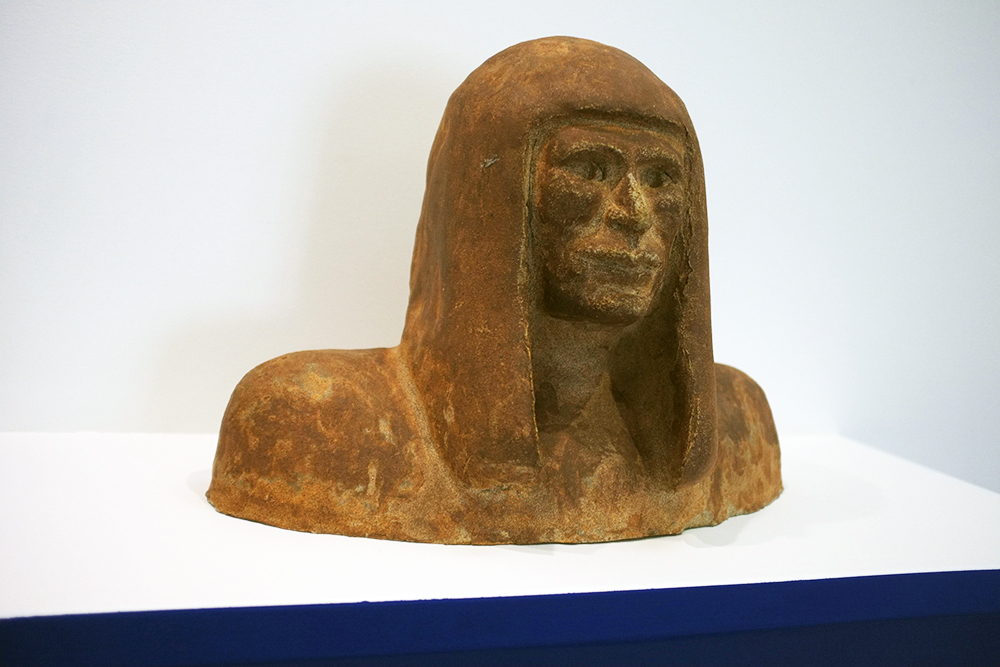
Collect install Assemblage no1 oyster shells, 2023 (detail)
mixed media including clay and crushed oyster shells
photograph by Yeshen Venema
In the context of art history, sustainable ways of creating have been around since the birth of conceptual art in the 1960s. Take German artist, Nils-Udo, whose plant creations placed in nature were left to develop and subsequently disappear as a way of commenting on the links between nature and humanity. Today, as we are faced with the sobering realities of humankind’s impact on the planet, environmentally-conscious art forms are becoming increasingly widespread. By working with found objects, natural and upcycled materials, and through processes that intentionally avoid damage to the Earth’s resources, artists are using their creative expression to highlight environmental degradation and the stark reality of climate change.
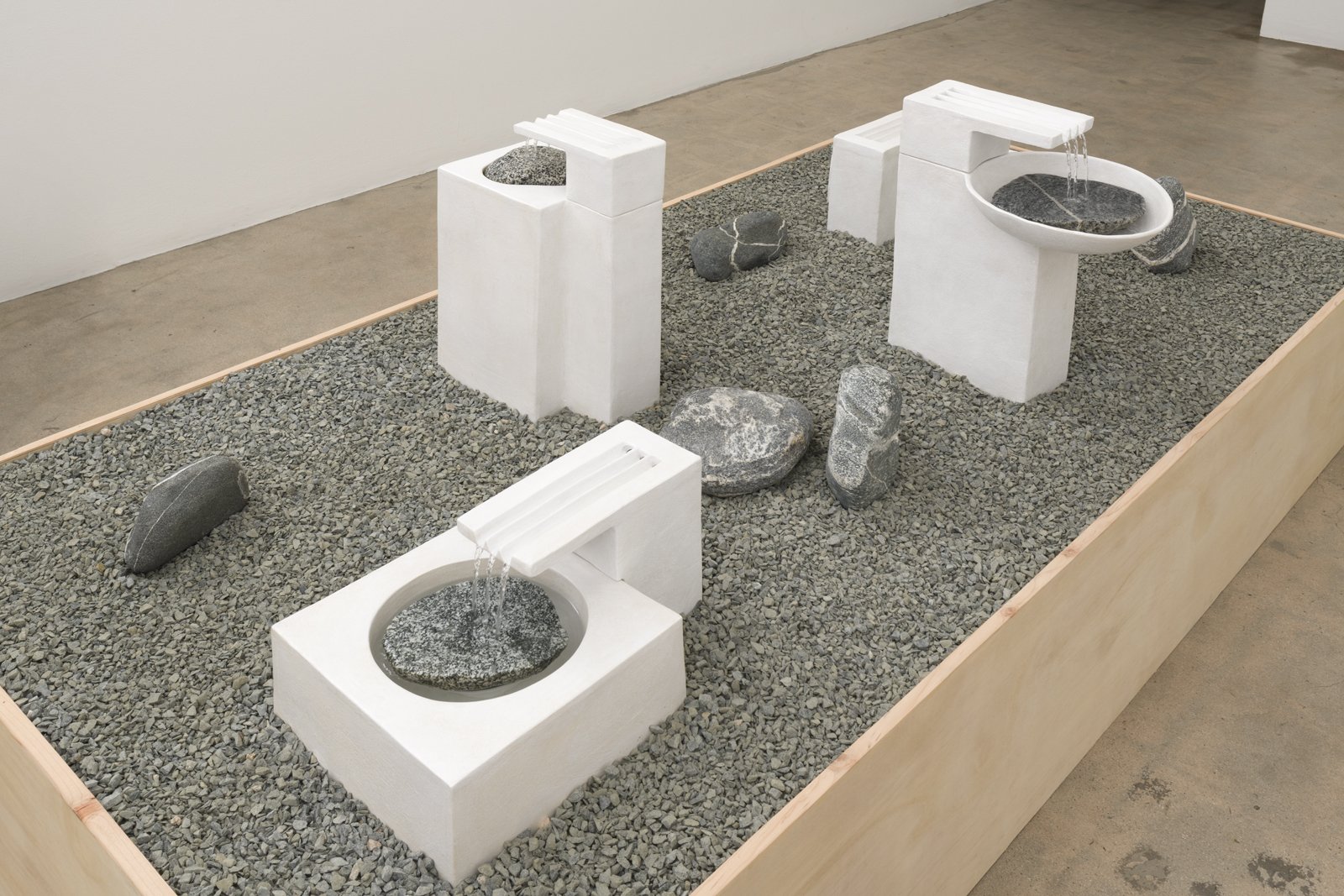
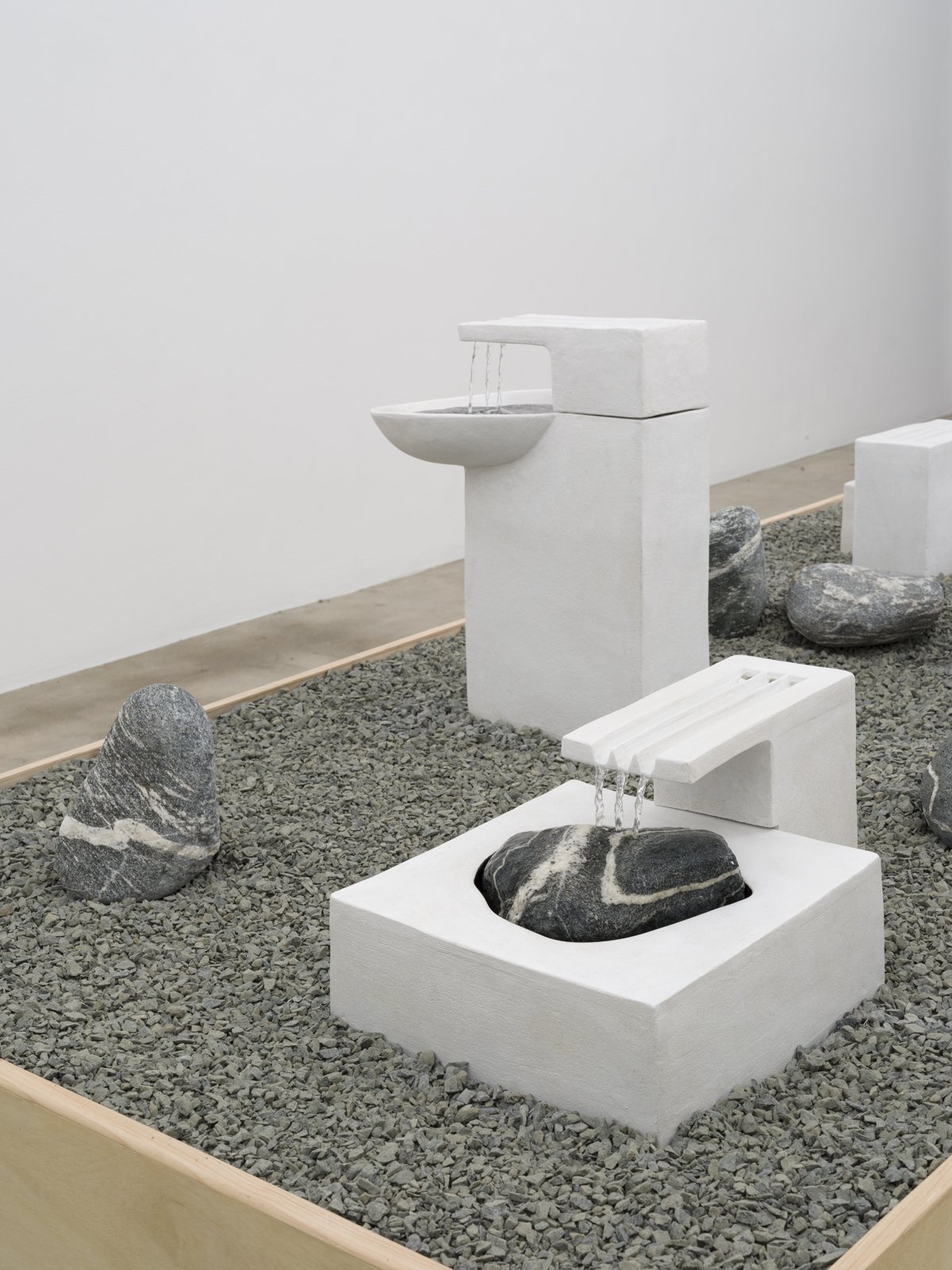
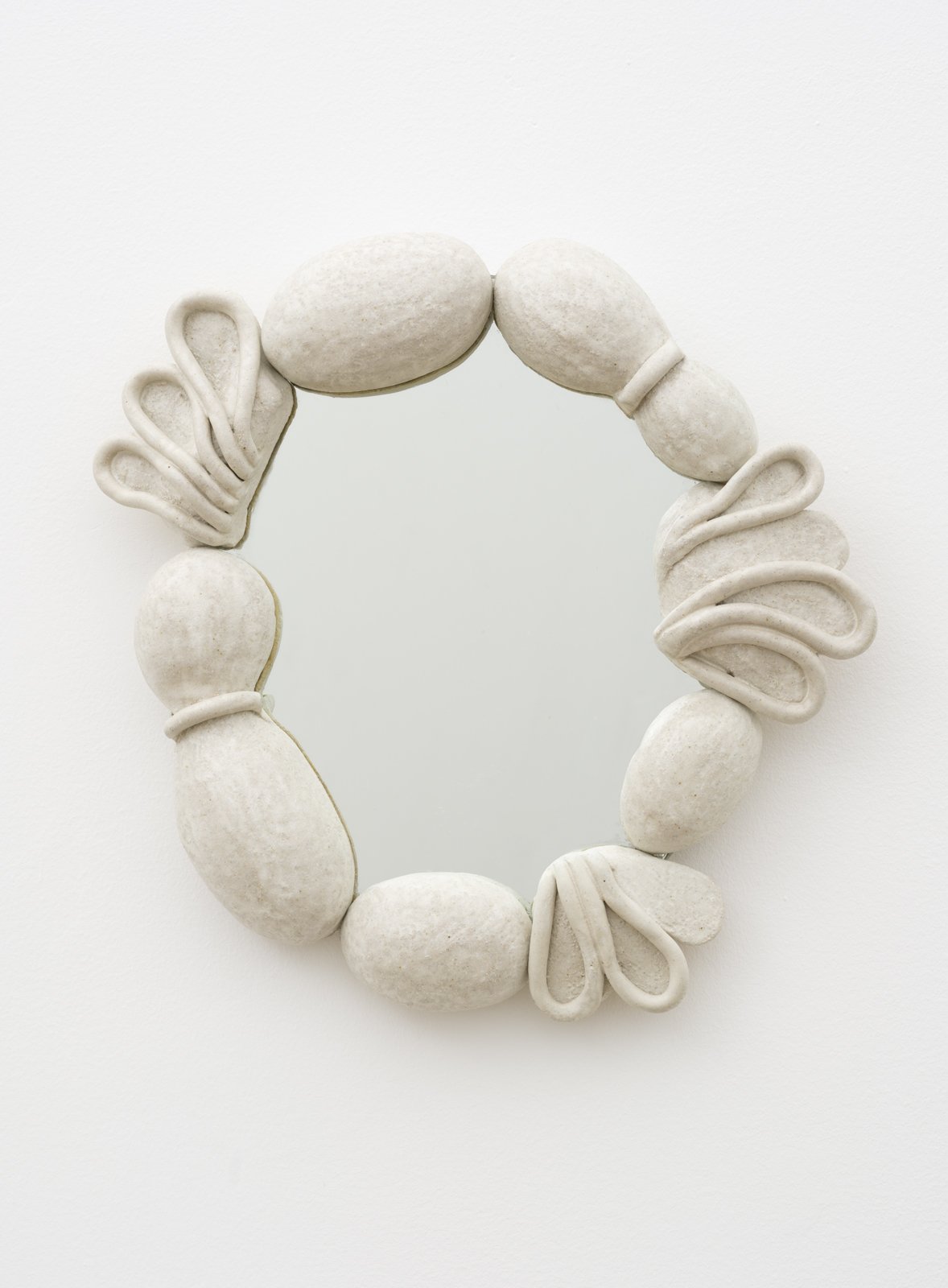
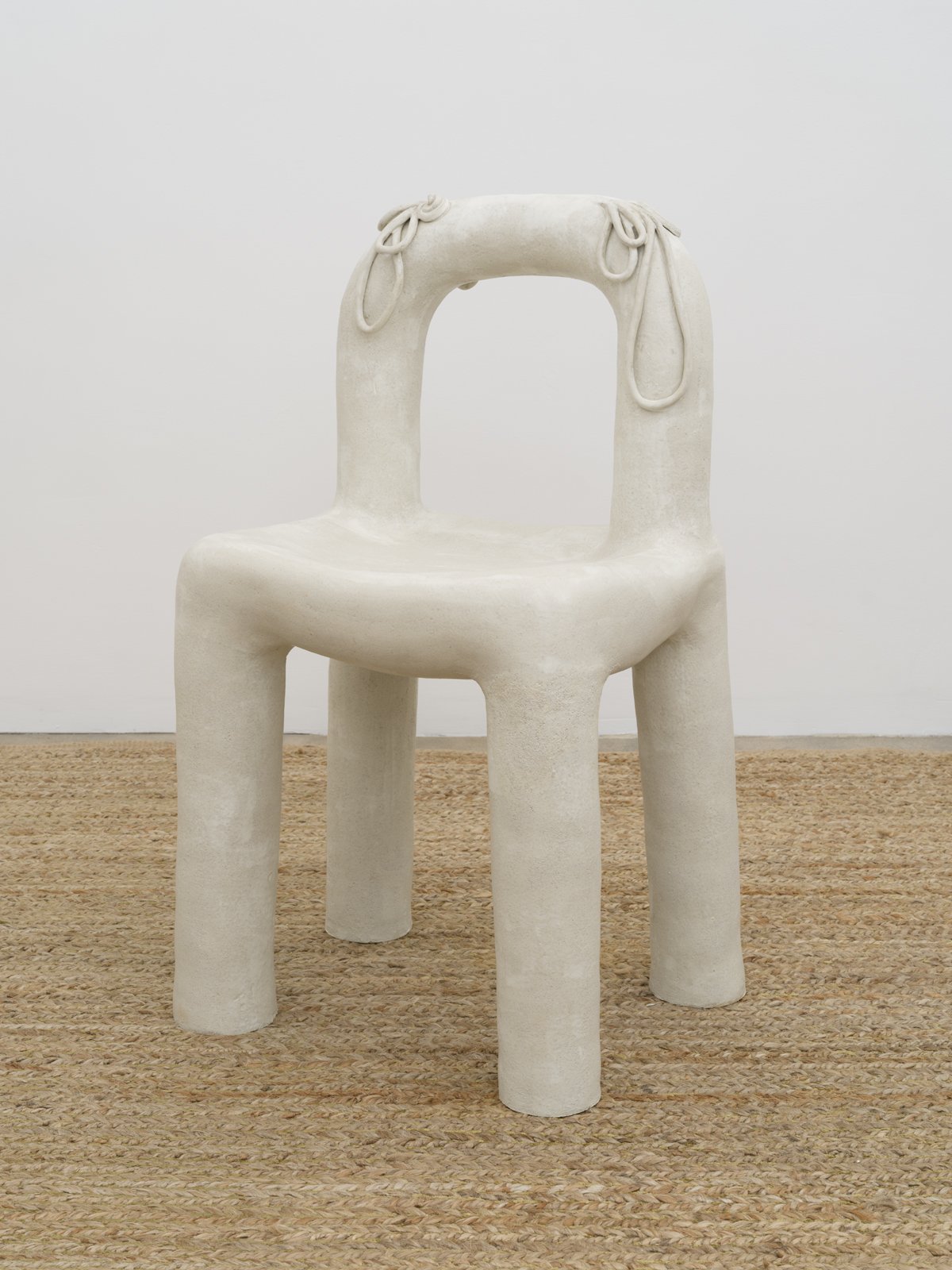
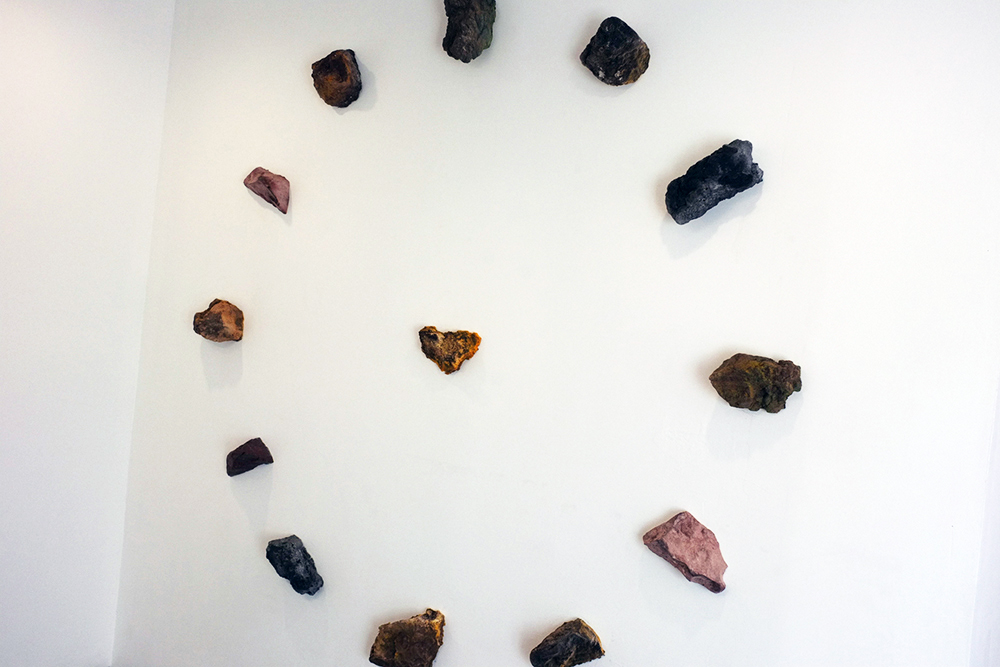
Margate-based artist Louise Frances Smith worked mainly with clay until she became increasingly concerned and frustrated with the unsustainable plastic packaging used to store her medium of choice. After conducting considerable research, it became clear to her that it was not possible to naturally source clay from her local area, so she decided to get creative and utilize what was available, better yet, she used what was in abundance: seaweed and oyster shells. Smith has spent the last two years collecting and experimenting with both as part of her newly adopted approach to creating sustainable work.
This year, as part of Somerset House’s 2023 Collect, Smith exhibited Sargassum Tide, a new body of work that examines wireweed seaweed and Pacific oysters, two non-native species thriving on the UK coastlines due to climate change. She subsequently presented the series in a solo show at The Margate School where she facilitated workshops on how to work with sustainable materials in collaboration with community groups, families, and creative practitioners.
In the following interview, Smith shares her journey with adopting a sustainable art practice, discusses the scientists, artists, and experts that have inspired her, and where she hopes to take her sustainable practice in the future. Read more.