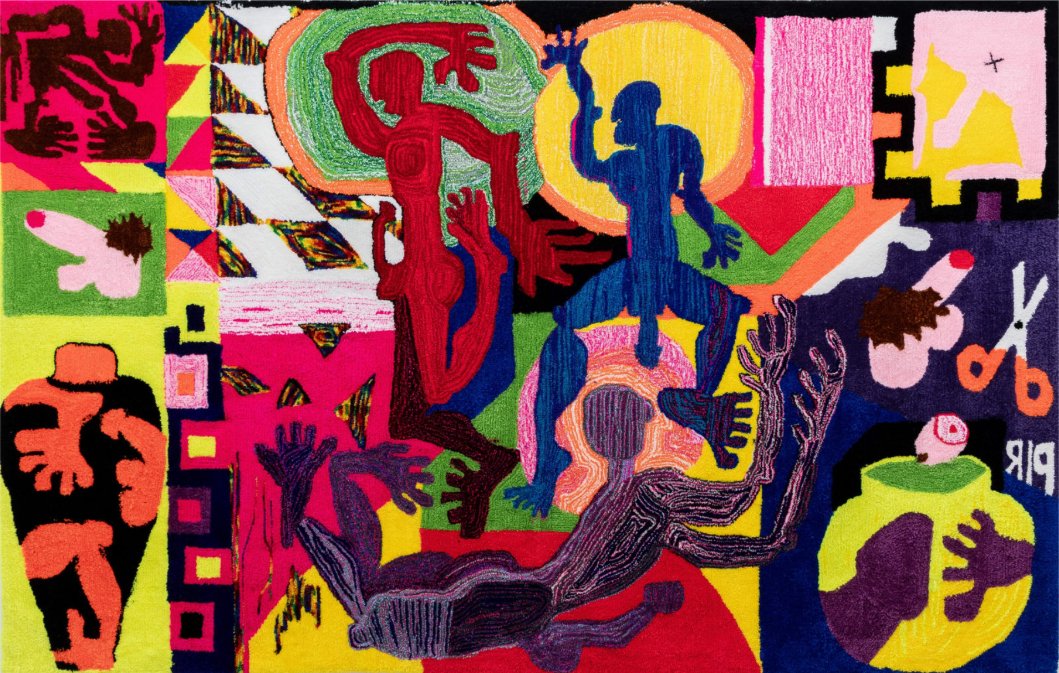
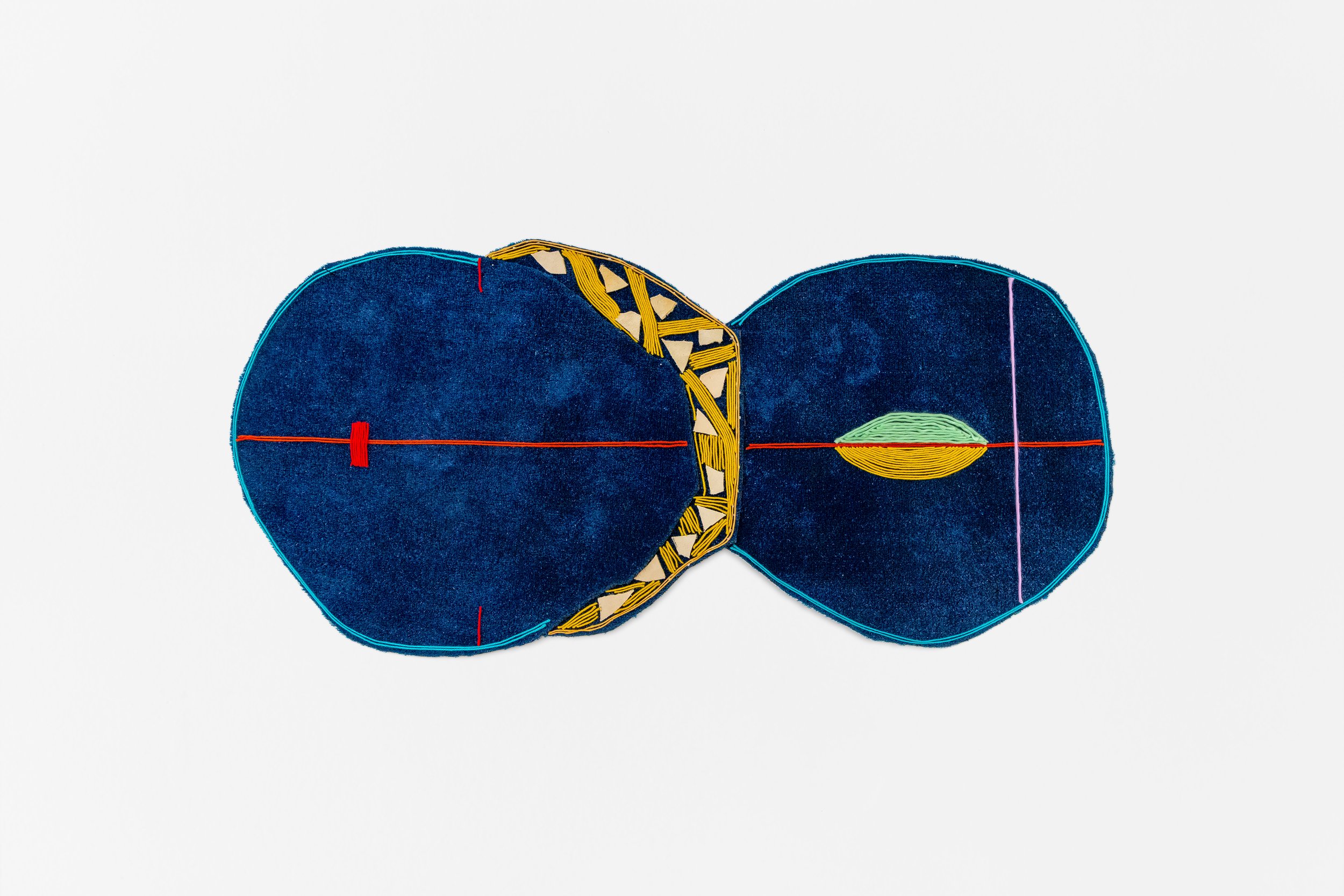
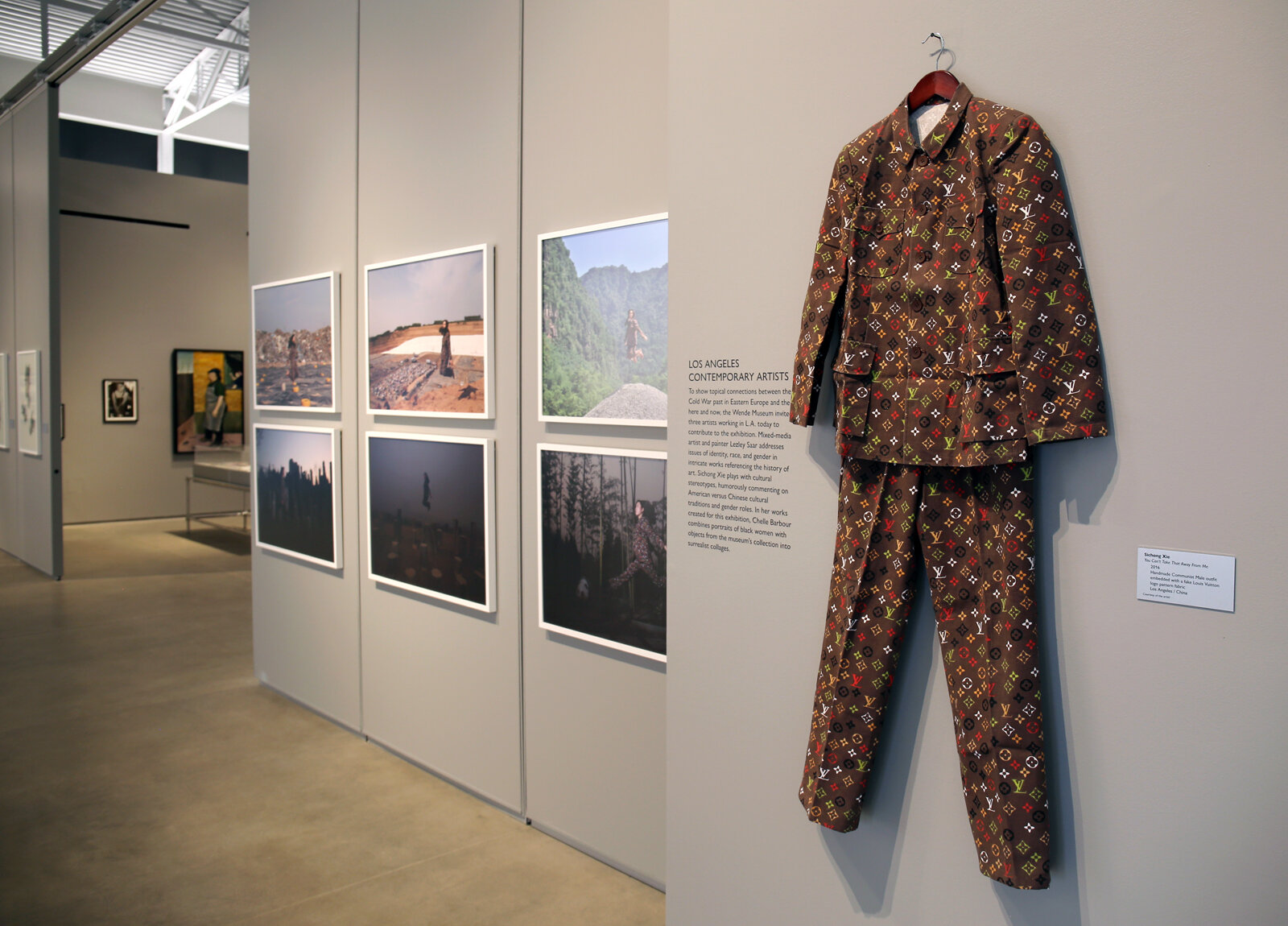
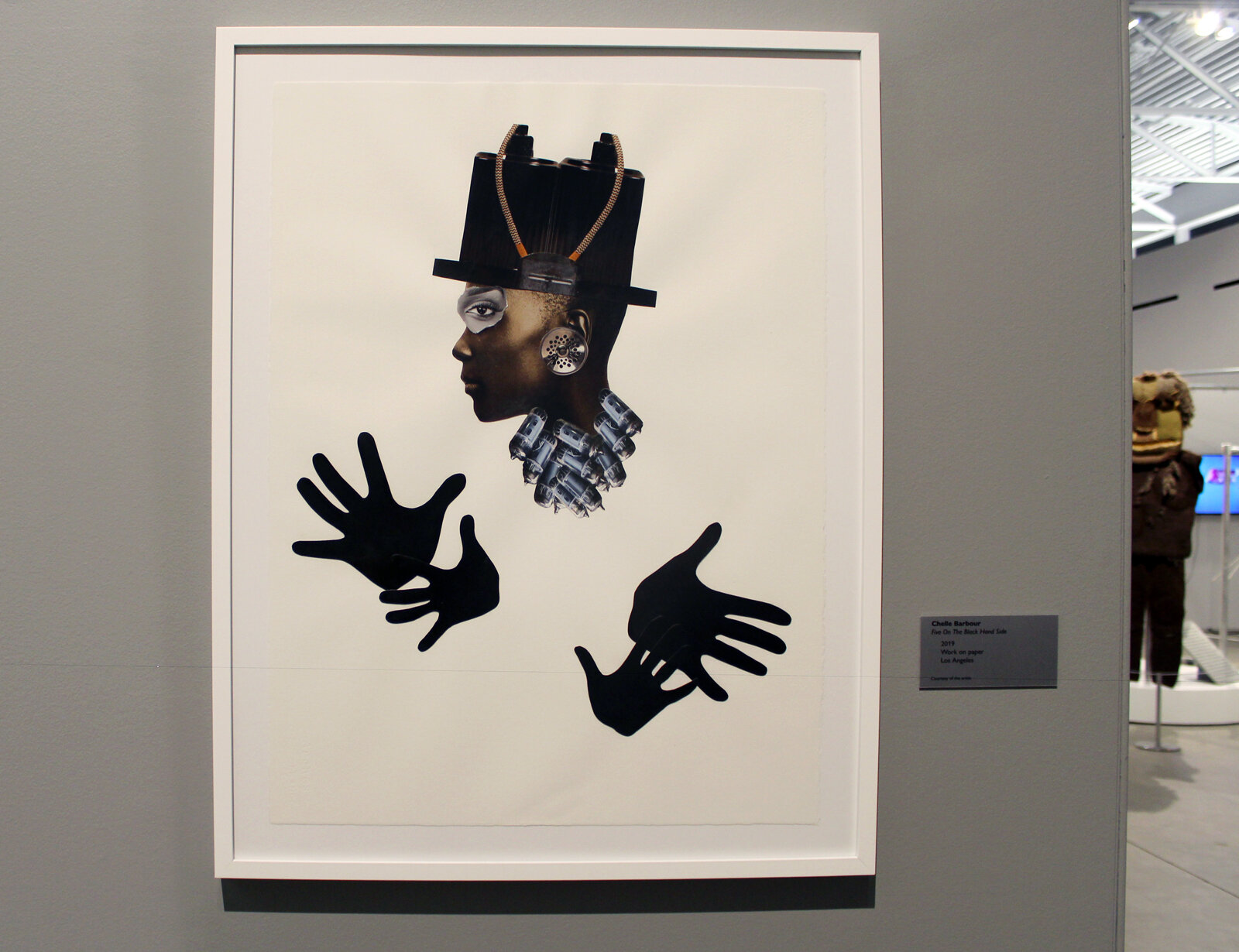
Dawn Williams Boyd
Abduction, 2025
Assorted fabrics and cotton embroidery floss
45 x 67.5 inches
text by Hank Manning
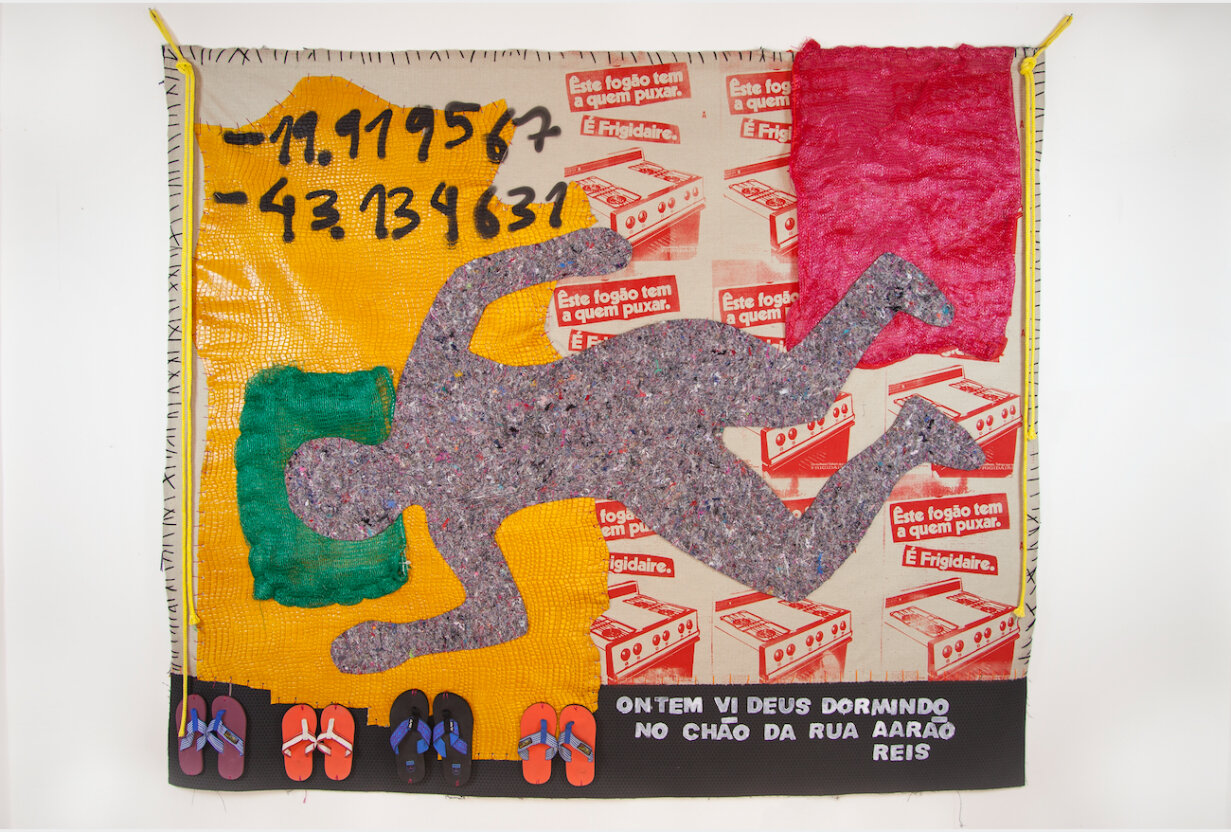
In FEAR at Fort Gansevoort, Dawn Williams Boyd inverts American history, imagining a parallel universe where Black oppressors imported white slaves and have maintained an economy predicated on race-based exploitation for centuries. Her cloth paintings, made with textiles imported from Africa, all closely resemble canonical American ephemera, including historical photographs and advertisements. Maintaining this color-inverting framework, the gallery, for its third solo exhibition with Boyd, has painted its typically white walls black.
The exhibition quickly succeeds in making us hyperaware of our racial biases. The scenes depicted—enslaved people chained together on ships, hooded horsemen celebrating lynchings, peaceful protestors attacked by police and civilians—are so ingrained in our memories that we instinctively assign roles before noticing Boyd has reversed them. Even knowing the artist’s intent, standing before these explicit works, our minds still resist the uncanny world she constructs.
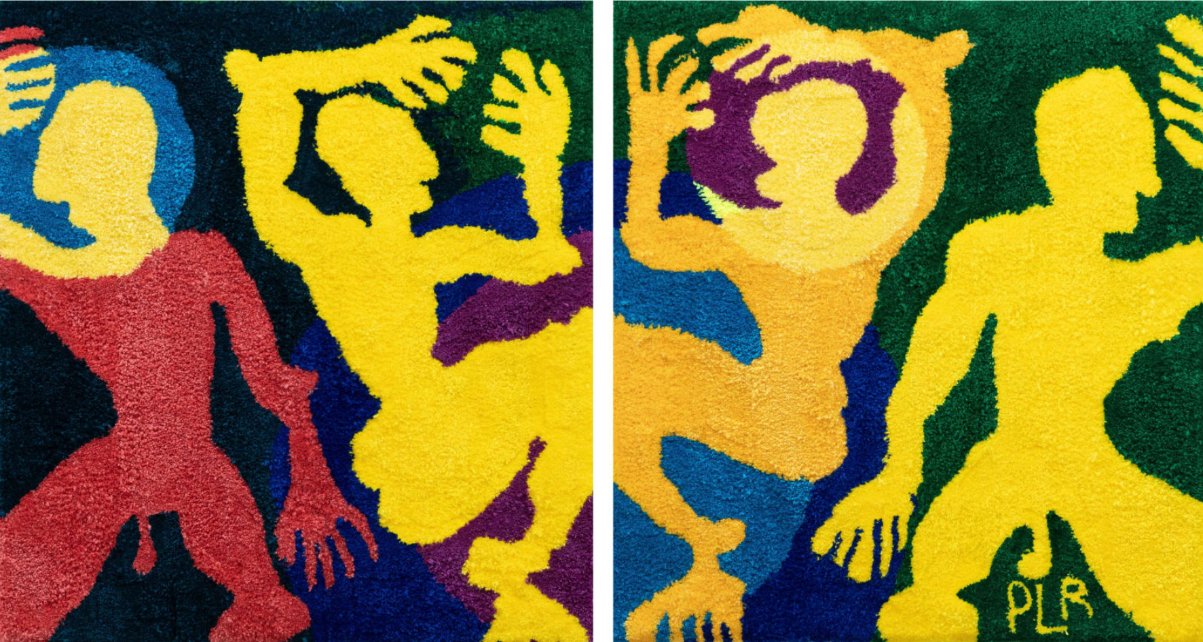
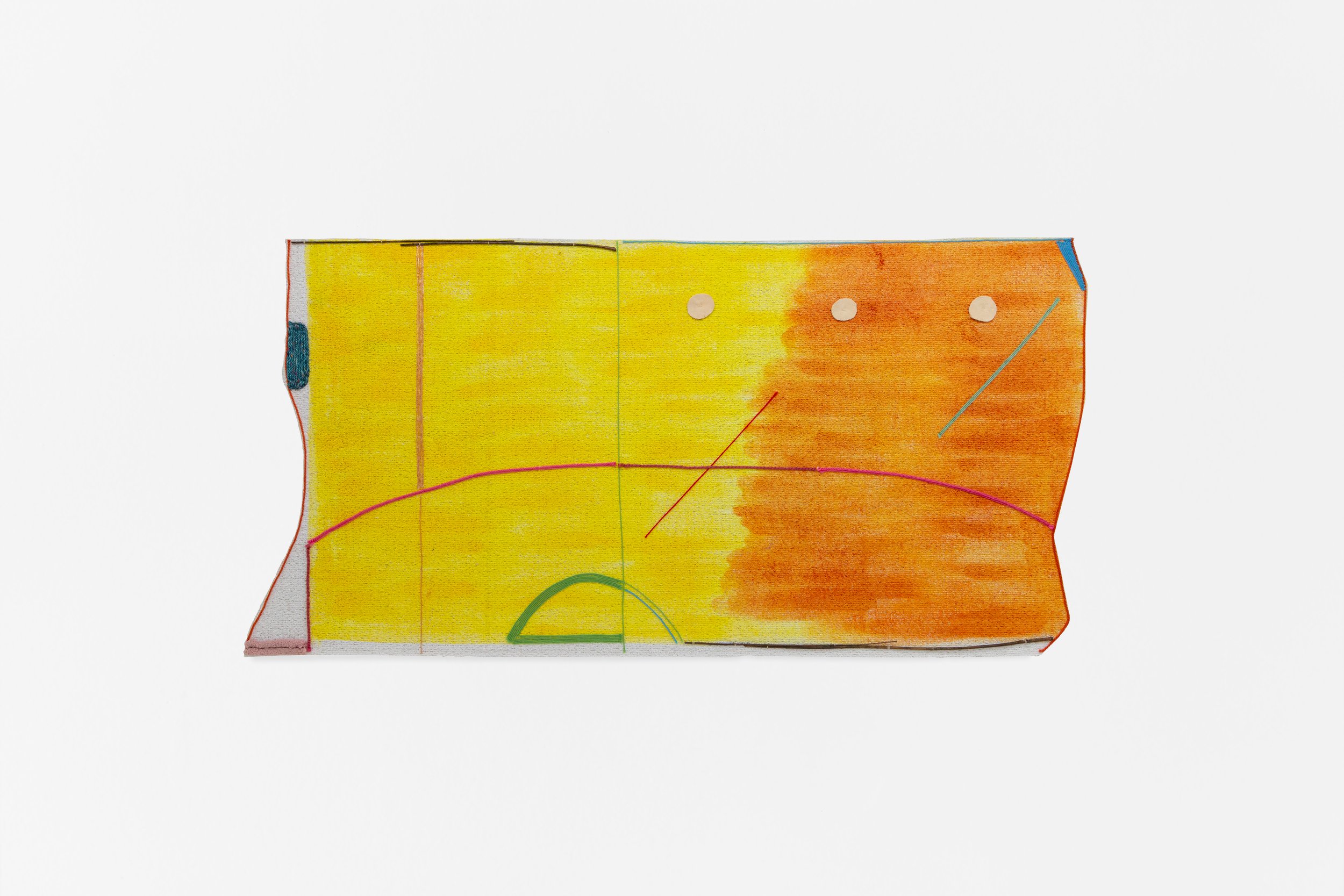
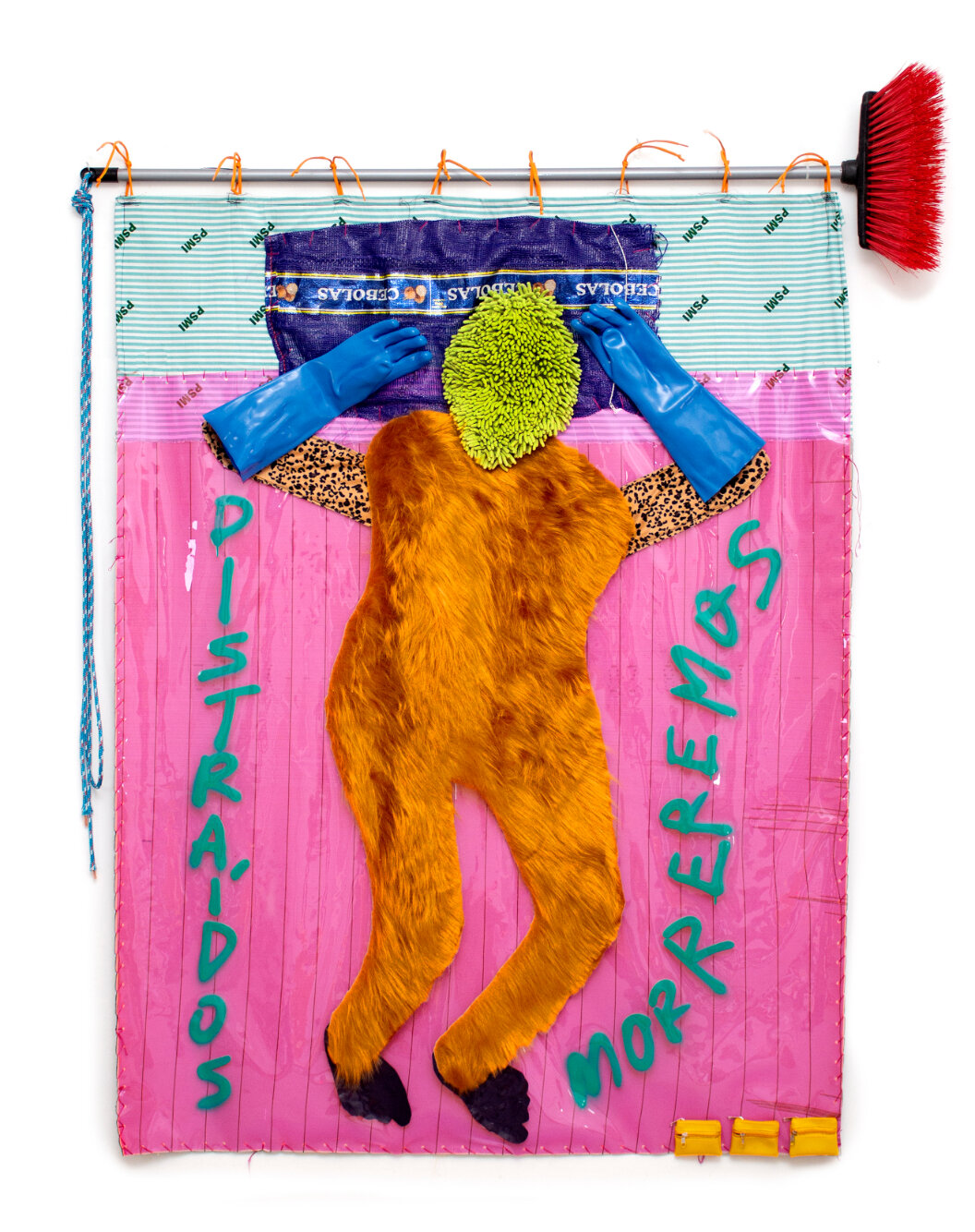
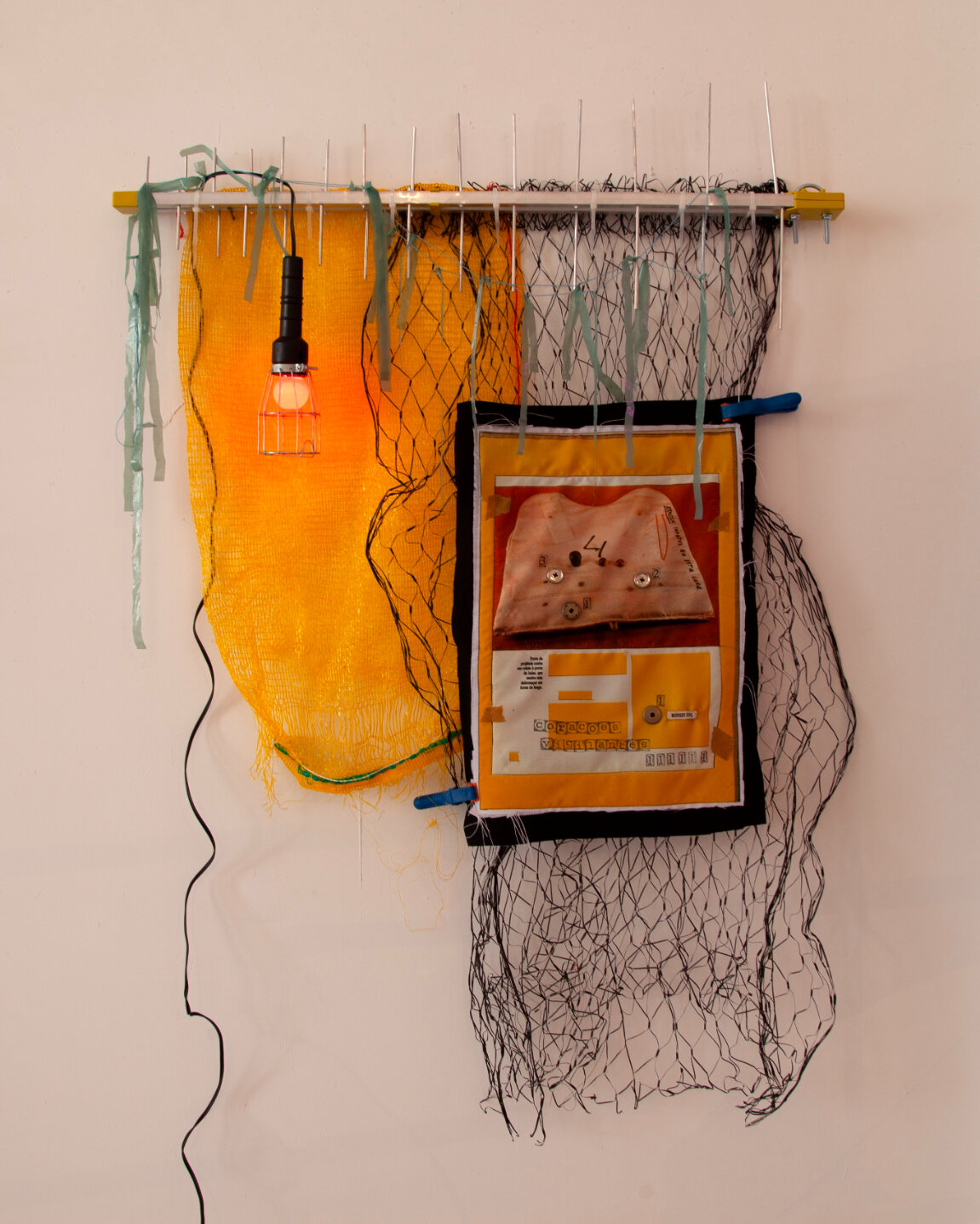
Dawn Williams Boyd
Brainwashed, 2025
Assorted fabrics and cotton embroidery floss
66 x 43.5 inches
In addition to these violent scenes, Boyd highlights the psychological violence that racism perpetuates in relation to the commercialization of cultural tropes. In a piece titled Brainwashed, a young Black girl, holding a black bar of soap, asks a white slave, “Why doesn’t your mamma wash you with Fairy Soap?” We are directly confronted with the immediate qualities we assign to the colors black and white, as well as how these perceptions affect one’s feelings of self-worth, particularly when learned at a young age.
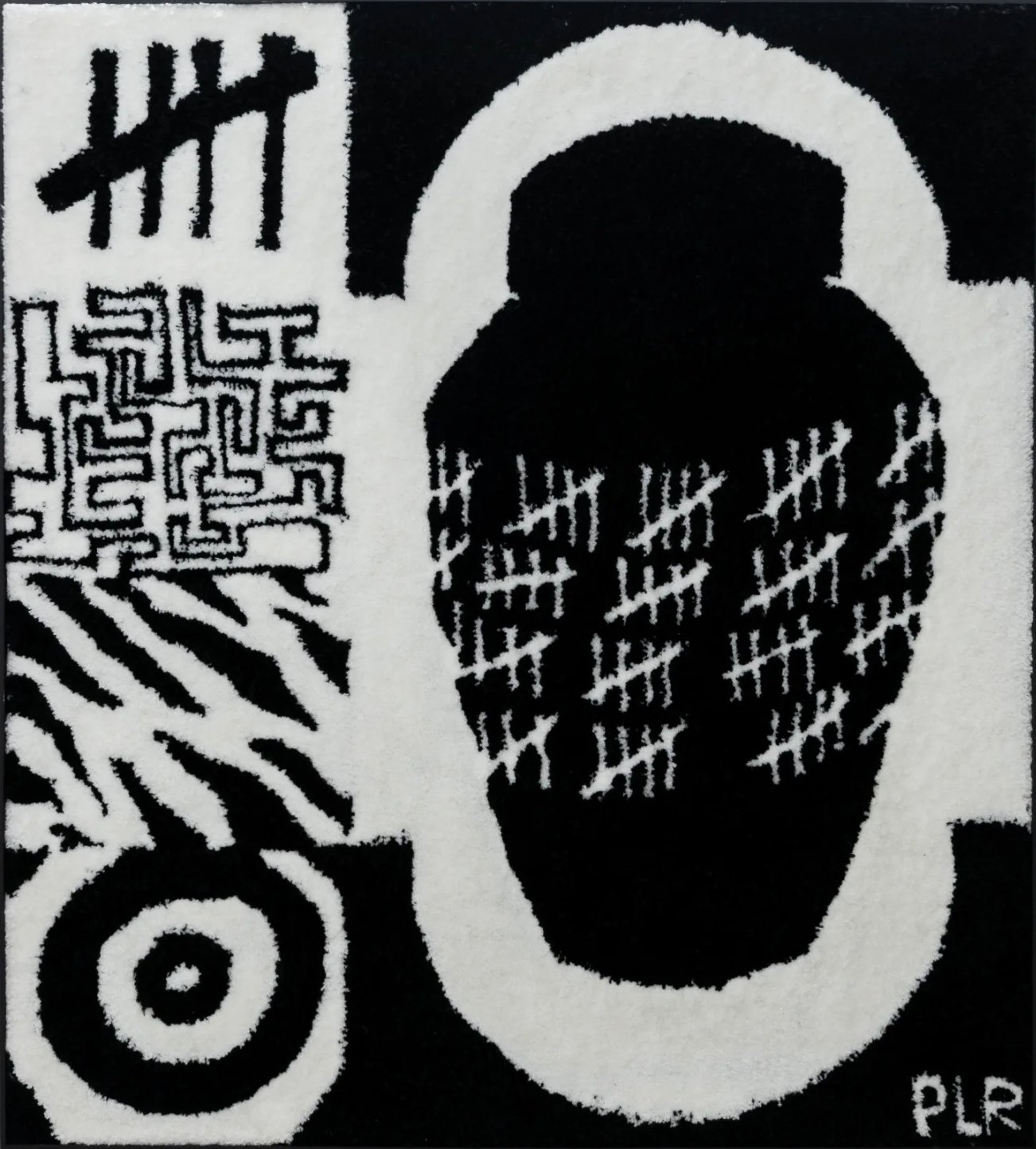
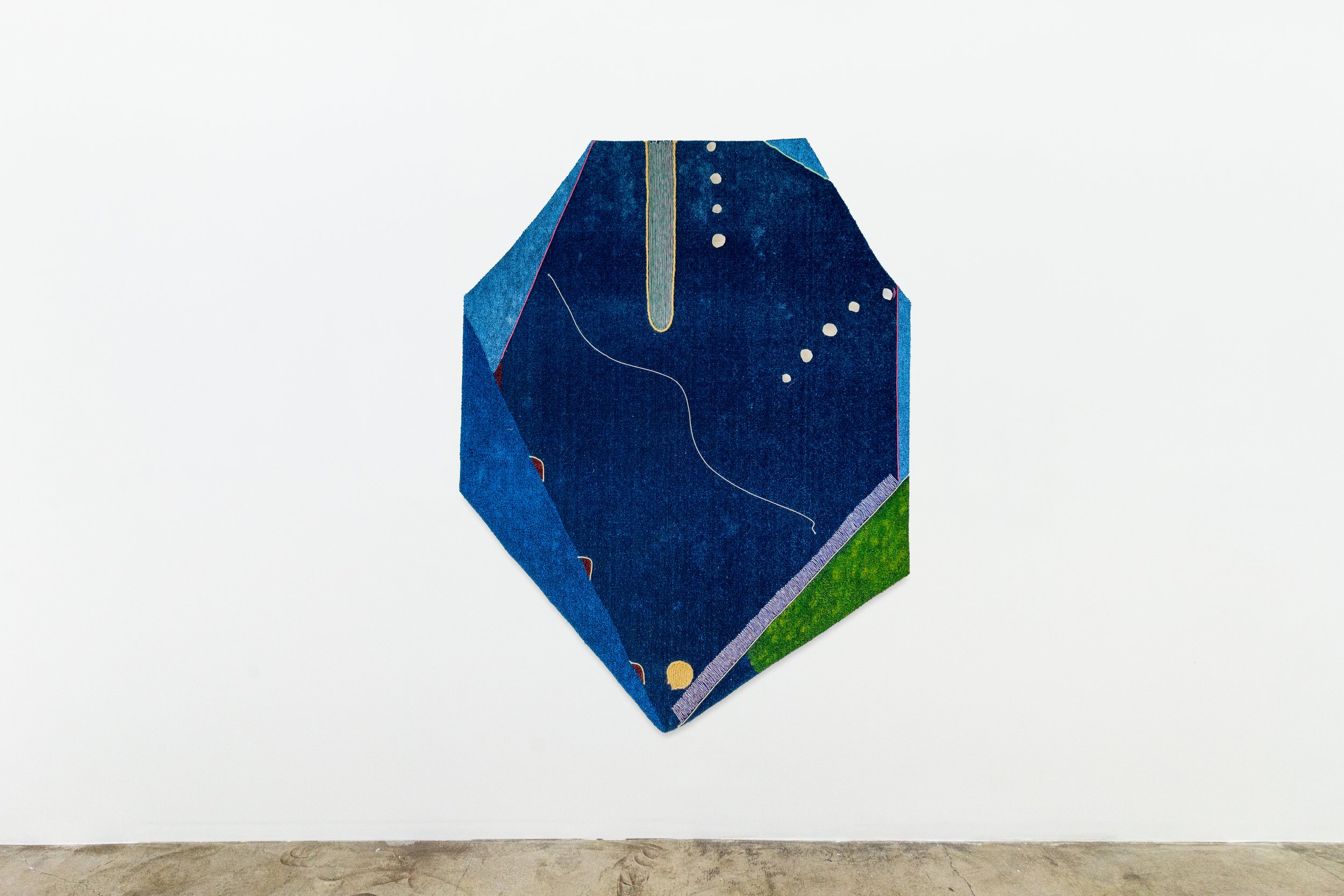
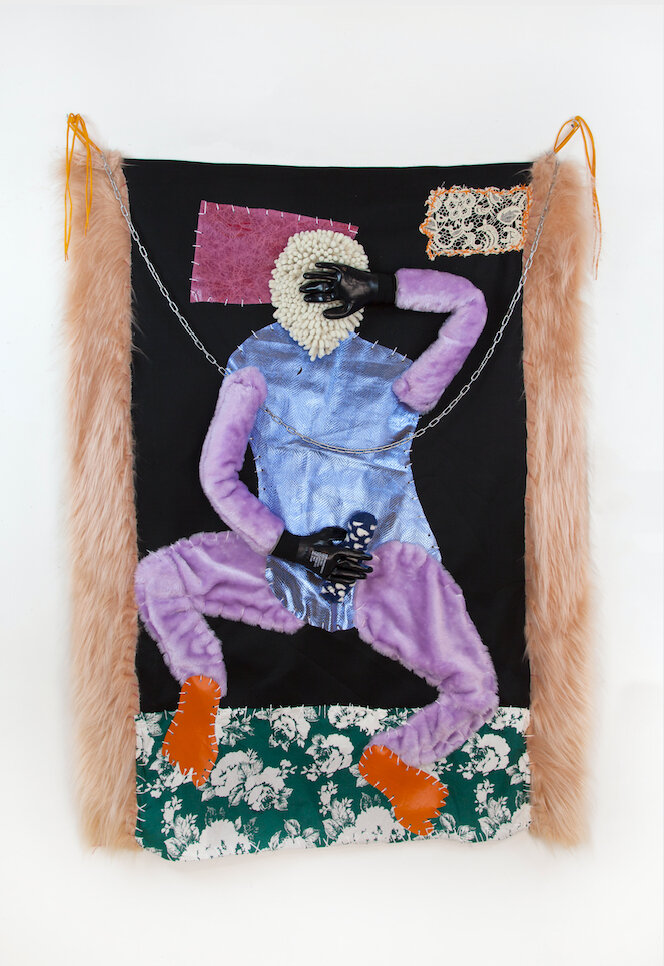
Dawn Williams Boyd
Cultural Appropriation, 2025
Assorted fabrics and cotton embroidery floss
47 x 58 inches
More than 150 years after the de jure end of slavery in America, economic and social inequalities persist. In keeping with this reality, Boyd’s textile works generally proceed chronologically through history, but they offer no hint of progress toward integration or equality; the racial divide remains unambiguous. She further underscores the role of seemingly benevolent industries, like entertainment and medicine, in perpetuating racial inequality. We see white subjects forced into society’s most exploited roles, from dancing in banana skirts in service of the hegemonic class (at a Prohibition era nightclub in Harlem), to being the subjects of gruesome gynecological research (imitating the work of Marion Sims, the “father of gynecology” who performed studies on enslaved Black women). In the real world, Black patients disproportionately lack access to the advances their exploitation made possible.
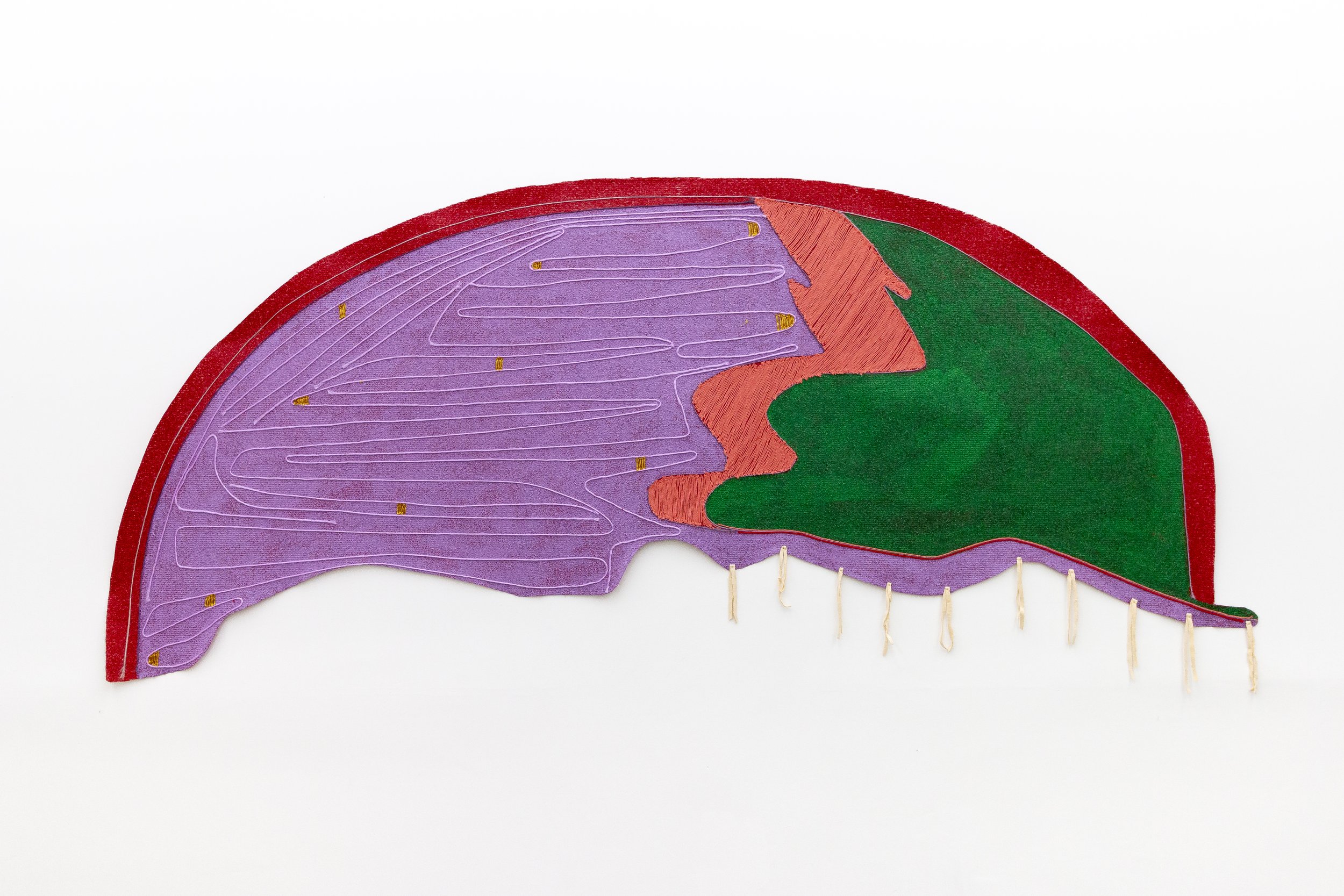
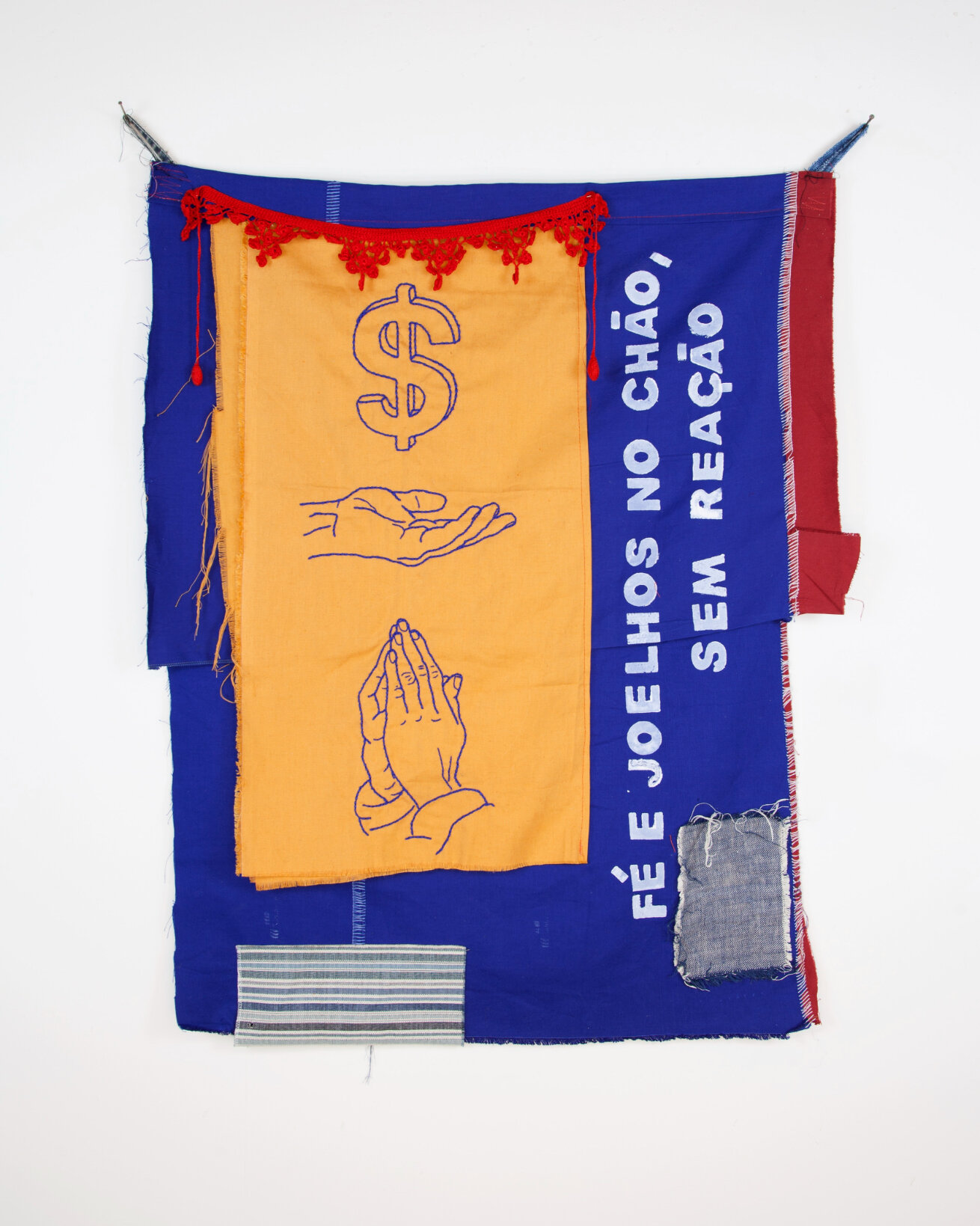
Dawn Williams Boyd
The Lost Cause Mythos, 2025
Assorted fabrics and cotton embroidery floss
56 x 70.5 inches
In The Lost Cause Mythos, a reframed Gone With the Wind features a white mammy serving a Black Scarlett O’Hara. Boyd addresses the power of art in shaping and reinforcing societal myths, however, she refuses to entertain the “happy slave” stereotype, instead portraying a despondent attendant. White characters lose their individuality; in settings from the beginning of the slave trade to the present day, men and women sport identical short blond hair and appear either nearly nude or in plain white garments. This homogenization dehumanizes them, treating them as props devoid of personality. Their Black counterparts, by contrast, have diverse hairstyles and elaborate clothing in a variety of colors, with red—here a symbol of power—especially prevalent.
Today, the US federal government and many state governments are attacking DEI initiatives, legal protections secured by the Civil Rights movement, and the honest teaching of American history, denigrating attempts to right historical wrongs as “reverse racism.” Boyd’s stark work puts these unsubstantiated claims into perspective. It asserts the degree to which most Americans underestimate the ongoing legacy of systemic racism and emphasizes the role of emotion in our material world. We see fear in the eyes of everyone, from those experiencing the horrors below deck on slave ships to a fragile ruling class who feels existentially entitled to their privilege and is terrified of losing it.
Dawn Williams Boyd: FEAR is on view through January 24 at Fort Gansevoort, 5 Ninth Avenue, New York