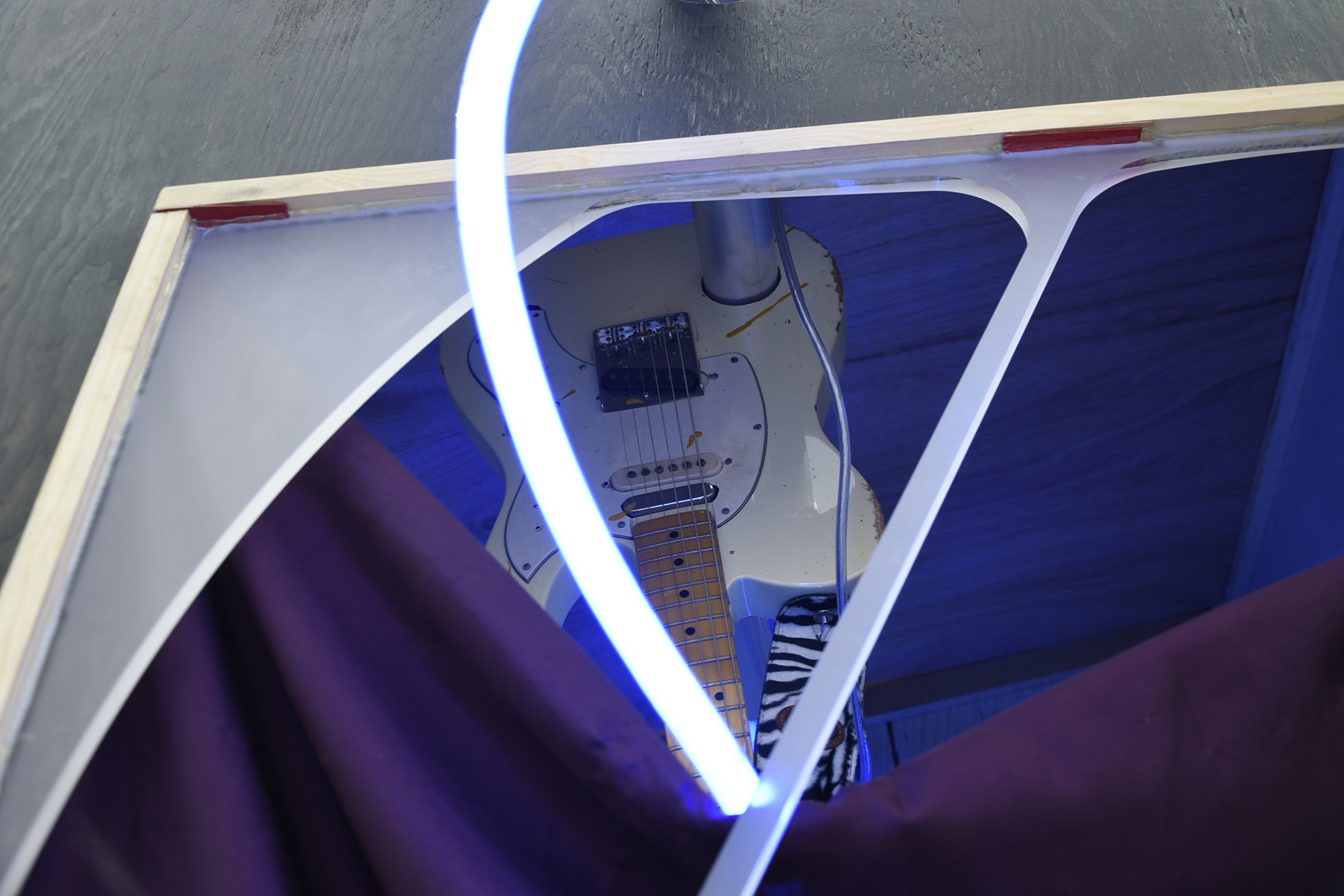
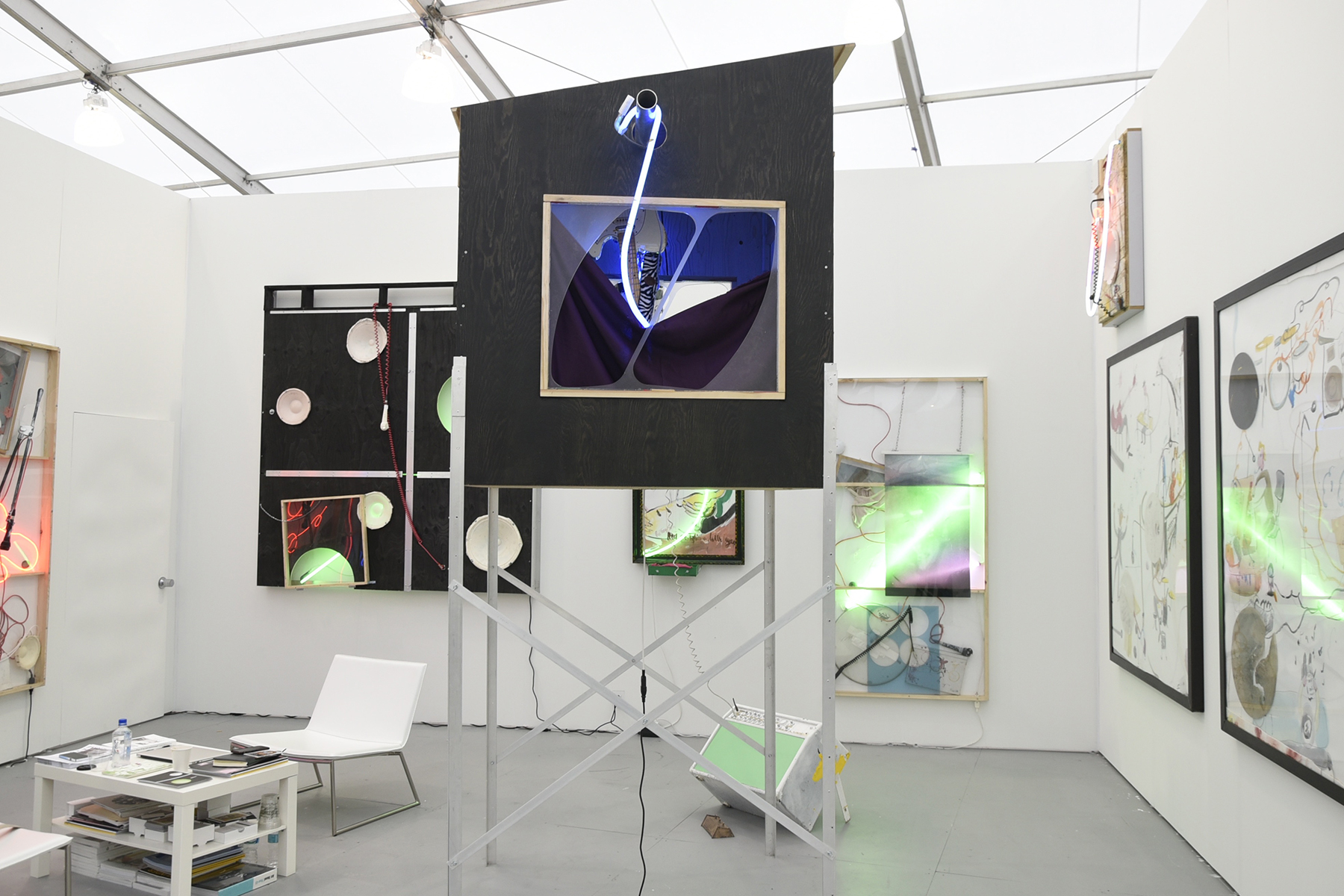
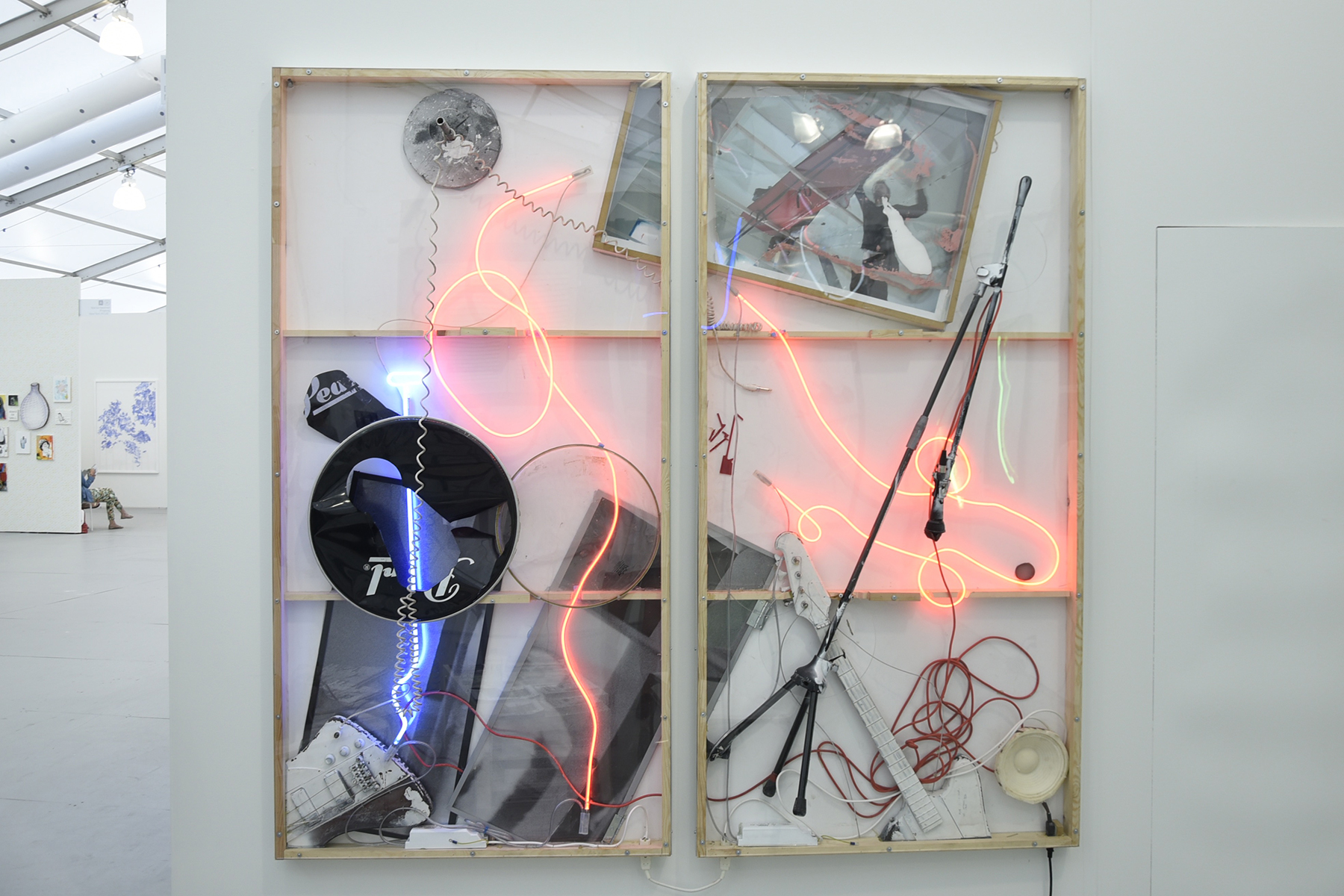
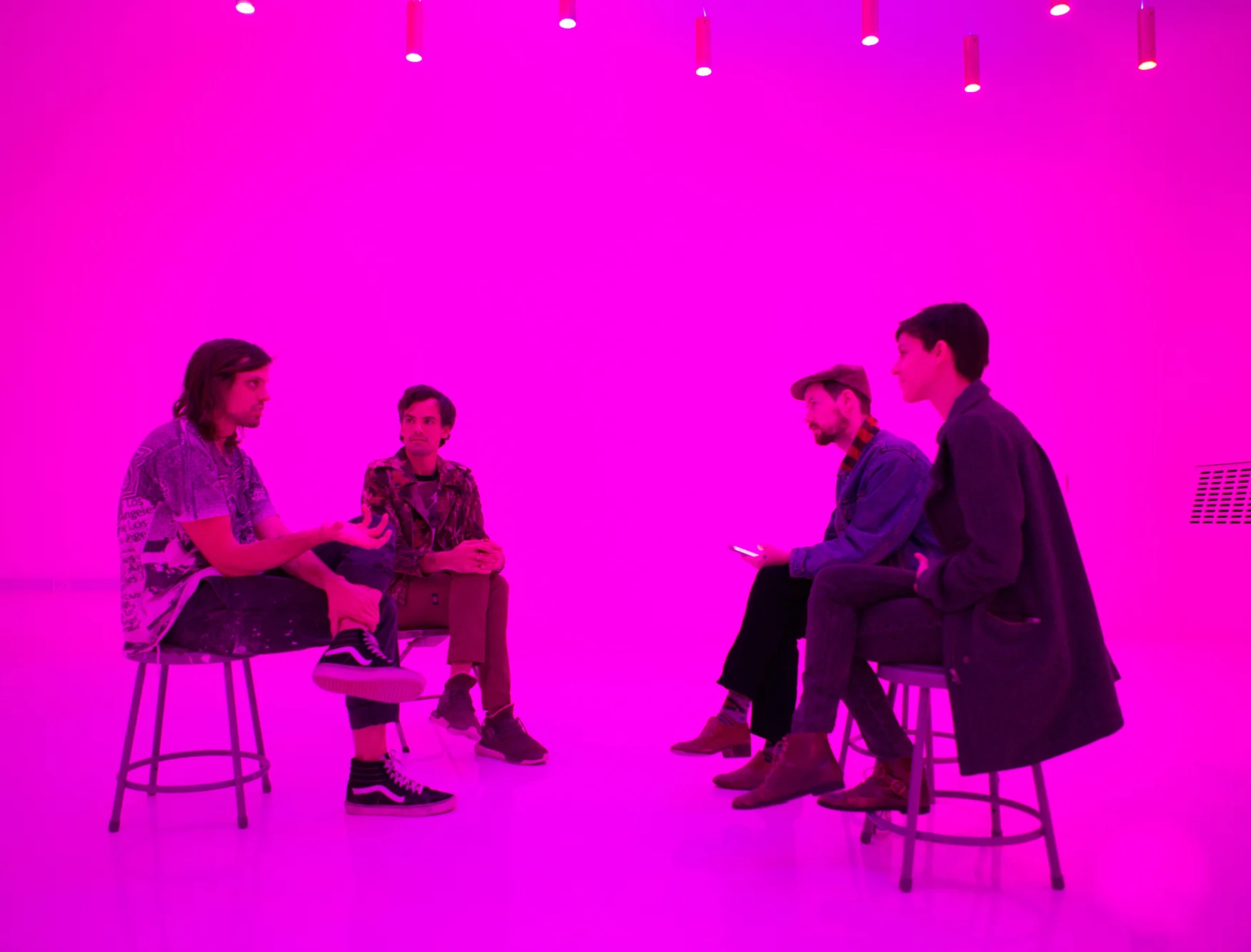
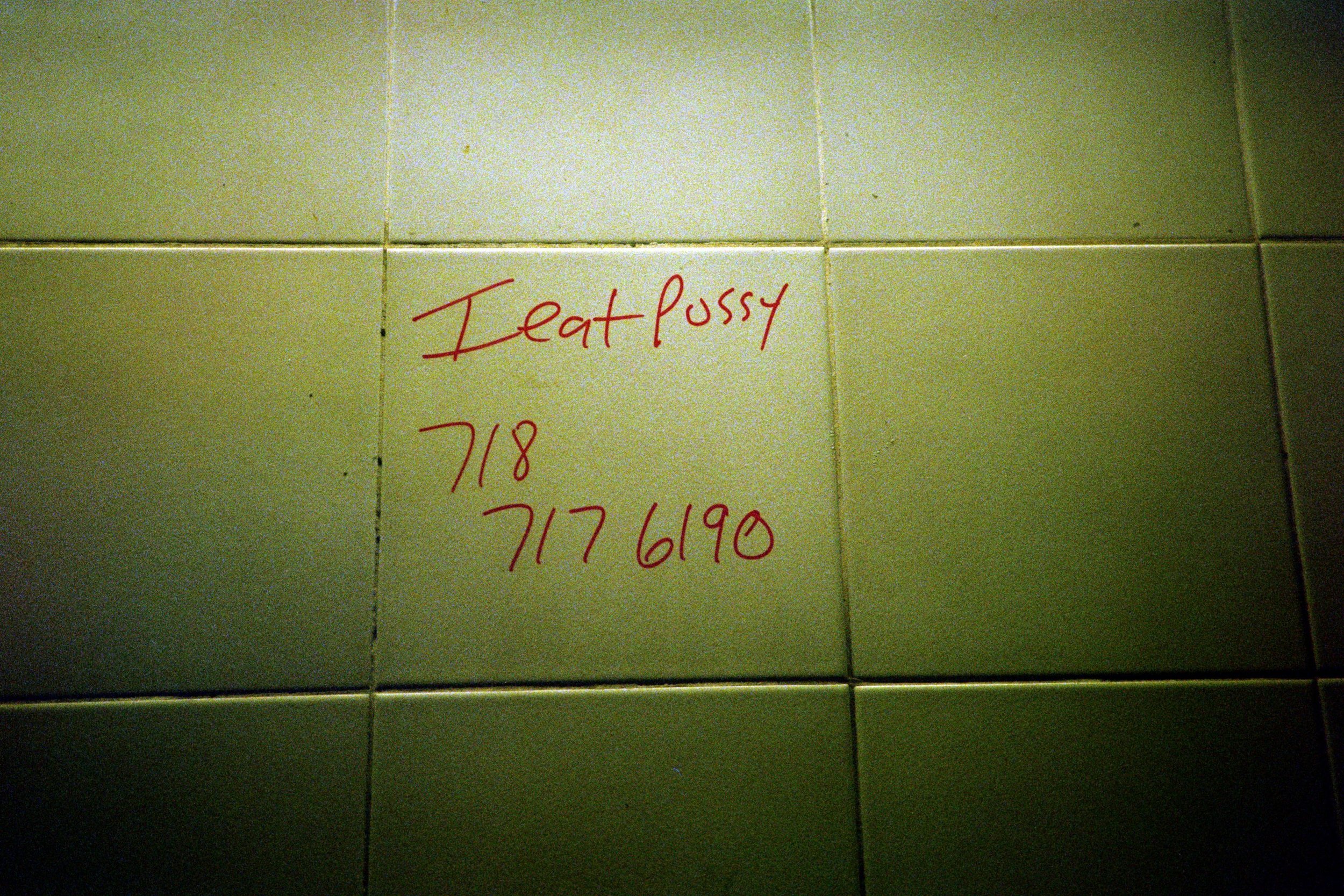At SPRING/BREAK Art Show earlier this month, I stumbled upon 1985 Artists’ booth, Glory Hole. Within that space, was a young woman’s bedroom. It seemed a stereotypically normal woman’s bedroom at first: clothes, underwear, makeup, and fashion magazines. Upon further examination, there were some alarming items contained within said room. There was a wall covered in erect male penises. This woman owned an extensive collection of gore horror films. There were knives and other weapons. Perhaps most nerve-wracking of the items was a shrine to the Los Angeles-based Satanist serial killer, Richard Ramirez. But even then, one doesn’t want to judge. In this art world of ours, we probably all know someone like this, obsessed with horror and listening to Norwegian black metal. Doesn’t mean they are crazy right? RIGHT? In this case, not so much, a TV reveals the whole story. The items belong to a predatory web cam girl, who lures men in through her web cam service only to fuck, murder, and cannibalize these men upon their arrival.
The installation was created by filmmaker Remy (yes, granddaughter of Tony) Bennett and Broadly writer Anna del Gaizo based on their short film shown at the installation, entitled ‘Eat Me.’ The film and subsequent installation are not without themes: desensitization, violence, anonymity, and social isolation among them. But Bennett, who gained indie film notoriety for her Lynchian romance ‘Buttercup Bill’ has been a horror obsessive her entire life, and really just wanted to make a gruesome and gory film. She found her story when she learned of her high school friend del Gaizo’s real life exploits in being a web cam girl. Del Gaizo gets to fictionalize her own experience in her performance in the film, and Bennett gets to create the horror scenario that she has dreamed of since childhood. The pair is still looking for funding to increase the length of the film, but I had to take the time to talk with them about this fascinating project. It was a fun conversation.
ADAM LEHRER: Remy, When did you get interested in horror movies?
REMY BENNET: Since the day I was born (laughs). I was looking at our high school yearbook, and my yearbook page is just a picture of Motel Hell. I started making horror films in the seventh grade. I was obsessed with the slasher drama. I would be running up and down the stairs with a camera in one hand and a knife in the other trying to get a POV, and my dad would have to stop me.
ADAM LEHRER: Was “Eat Me” conceived as a film first or an installation?
BENNETT: A film, which is actually something that I’m still working on to make it longer.
LEHRER: So what made you want to live in this world longer with the SPRING/BREAK installation?
BENNETT: Design is a big part of the film. I’m interested in the stories that objects tell, and how much of the story comes from characters surrounding those objects. We thought there was detailed story to tell with her belongings.
LEHRER: It reminded me a bit of what Elmgreen & Dragset do. They set up these sets, and there are all these clues around, so you find out about who the character is.
BENNETT: I’ve always been a fan of that kind of art, like Sophie Calle. You’re being put in the role of this forensic investigator, and you’re collecting these clues.
LEHRER: Was it interesting to see people interacting with your things?
BENNET: It is our personal belongings. It’s weird. You’re talking about yourself while simultaneously talking about a character. It’s fun!
DEL GAIZO: The character’s style is essentially a curated version of my own. Aside from the cannibalistic serial killer aspect, there’s a lot of me.
LEHRER: That was what was so cool about it. When I saw it, first I’m thinking, “I’ve seen girls like this before. She’s a young girl, she’s into sex, she’s into drugs. She’s snorting coke. Maybe she has a problem.” I didn’t find that there was anything out of the ordinary for a woman of a certain age. But then you find out that she’s a murderer. Was that something you were interested in?
BENNETT: I really set out to make a film about sadism and cannibalism. That was the main goal.
LEHRER: Speaking of, I was also curious what you might think of this movement of these artier high-concept horror films: ‘The Witch,’ ‘It Follows,’ ‘The Babadook,’ and all those. Like I thought ‘The Witch’ had some good ideas, with the joining the witches at the end being the good ending.
BENNETT: Well, I like traditional gore movies like ‘Blood Feast’ and ‘Wizard of Gore’ by Herschell Gordon Lewis. That’s what I wanted to do. Do you listen to Bret Easton Ellis’ podcast?
LEHRER: Yeah, he hates those movies.
BENNET: (laughs) Yeah, I liked his podcast with Eli Roth, and I liked what he said when he was like, “if someone has talent, and ideas, that should be nurtured.”
DEL GAIZO: Then again, Bret Easton Ellis did write ‘The Canyons,’ (laughs).
LEHRER: So part of the film is biographical, because Anna did some webcamming?
DEL GAIZO:. I thought I would probably turn it into some long-form essay or some sort of investigative journalism. I’ve always been interested in subtleties of human sexuality. If I’m going to research something, I’d rather just do it. In college, I got stuck in this class that I needed to graduate. It was a class about maids in popular culture, which is the most specific class ever. One week, we studied the eroticization of maids, so I went to work as a fantasy maid.
LEHRER: So you just like to immerse yourself?
DEL GAIZO: Yeah, it was a personal experiment. It’s kind of harrowing and soul-crushing. You have to be kind of a sociopath to be fine with it. I would just take these screenshots once in a while of the dialogue, like the shit these guys would say. It was hilarious and weird. One guy just paid me before I was even naked to give him the finger. Some guys just want to smoke pot with you.
LEHRER: Lonely dudes?
DEL GAIZO: Well, what also surprised me was that there were young, totally normal, cute guys.
LEHRER: I guess I imagine loneliness because if I really wanted to see a naked girl, there is so much pornography I could watch. So the live aspect seems like something else.
DEL GAIZO: Intimacy. That’s part of what’s really intriguing about it. It is virtual and hollow. Ultimately, I would just hang out in my room with a computer. It doesn’t actually feel real. But there is this intimacy. One guy just wanted someone to hang out and talk to. I was like his virtual girlfriend for a while. It wasn’t even overtly sexual. I talked to this kid for three hours because he didn’t know if he was gay or not and wanted to talk to a therapist
BENNETT: There were a lot of sweet people too.
DEL GAIZO: A lot of mega creeps too. A lot of daddy requests and little girl stuff. Things you would expect.
BENNET: I was a little bit tentative at first. I’m a fictional filmmaker. I was like, would you feel comfortable if I adapted your experience into fiction. She was like, of course!
DEL GAIZO: I was excited. It gave me a reason for doing it. I wasn’t just being a deviant anymore.
BENNETT: I always wanted to make a Henry: Portrait of a Serial Killer-esque kind of film. It’s a cold portrayal of this guy’s life, when he happens to be a serial killer.
LEHRER: Henry is a stone-cold killer, but the film give him an empathetic portrayal. We’re not exactly seeing an empathetic portrayal in this film, so what was appealing about Richard Ramirez?
BENNETT: She looks up to Ramirez like he’s a rock star. She’s also a Satanist. But I would definitely not compare her to a Dahmer, or even a Bundy. She’s much more like a stone cold psychopath.
LEHRER: Ramirez targeted women, he was sadistic. He would take anyone down.
BENNETT: He had a weird, but horrible, sense of humor. And the Satanist thing is such a statement. It’s such a teenage silliness. It’s like walking around wearing all black and listening to AC/DC like, “If you want blood, come and get it.” He was shameless.
DEL GAIZO: From my perspective, the fact that Richard Ramirez is physically attractive resonates. I saw the character as someone shallow and narcissistic; really into aesthetics and fashion – all that crap. This is terrible to say, but there is a reason why he had fans girls in the courtroom. He has the looks.
LEHRER: The piece also plays with perception so much. I know certain girls who might be into Black Metal bands like Darkthrone and serial killers who are not psychos. But that’s my age. Maybe a sixty-year-old woman, right when he sees the pot or the coke, is going to think something different about the character even before the sadism.
BENNETT: That was interesting to observe people’s thought processes. People were speaking out loud, which was so interesting. People would see the bloody sneakers and go, “Oh, shit. She’s coming for me!”
LEHRER: My girlfriend thought it was badass. She works in the corporate world. In order to define herself as a woman in that space, she has to go through all these back channels. Whereas this girl is establishing her aggression and herself in this totally overt way.
DEL GAIZO: These webcam customers are inviting this girl over to their homes. And that would happen. When I did this stuff, I was lying. I said I was living in LA. Guys were giving me their addresses in LA and saying, “Why don’t you just come over?” It’s very presumptuous to assume that I’m not a psychopath. That’s what we wanted to toy with. And she is this complete psychopath – this isn’t a rape revenge story.
BENNETT: The guy that we cast is a beautiful person who would express this deep loneliness in such a poignant way. Neither him nor Anna is a professional actor, but they’re really intuitive. He’s expressing so much love for this person because he’s so lonely. It was actually a beautiful thing, and she ends up killing him and eating him.
LEHRER: The killing was crazy enough, but when you see the eating, I was like, what?
DEL GAIZO: She makes protein shakes with the dudes!
BENNETT: Yeah, it has some humor to it. It’s not completely earnest, of course.
LEHRER: How much longer is the movie going to be than what we saw?
BENNETT: I’m going to aim for fifteen minutes. I just need to raise some money to finish it. It’s a total fucking B movie that we just threw together at first. But we’ve cared about it so much and researched it for so long that I just need to finish it. The rest of the film is going to be real emails that Anna has compiled, and we’ll have voiceovers that will be integrated into the film. You see the scenario play out with the voiceover.
LEHRER: I read in an interview before your first film came out with Bedford and Bowery, you said, “I’m not interested in making anything that doesn’t have to do with sex.”
BENNETT: That was taken out of context. It was extracted in a way that was weird. I think sex is such a basic component of art.
LEHRER: Is there anything in culture anymore that doesn’t have to do with sex?
DEL GAIZO: It’s so intertwined with every aspect of human nature. But when we were filming, we weren’t trying to make it sexy.
BENNETT: That wasn’t our goal. It’s about a sexual thing, but there was a conscious effort to resist eroticizing it.
DEL GAIZO: It’s for money, like most sex-related jobs.
LEHRER: It’s almost like it’s in direct opposition to the themes in your first movie, which was more about intimacy and jealousy.
BENNETT: I would say that film was a lot more earnest, in certain ways, about relationships and growing pains and childhood. I am a filmmaker who is much more interested in genre film – specifically horror – and how you can tell a story through those tropes. I like extremes. I think that sex can be like horror – it can be taken to the extreme, dosing it with humor and style.
LEHRER: Technology has entwined sex and violence more than it ever has, simply by the images you’re subjected to, that seems to be a theme explored in the film.
BENNETT: Sex has always been debauched, it’s just on the surface now.
LEHRER: Pornography is great in small doses, but a 13-year-old kid who starts watching hardcore porn is going to be fucked up by the time he’s 18 and has sex with someone.
DEL GAIZO: Definitely. He’s going to be confused that his girlfriend isn’t acting like a porn star. If I was fourteen and watching porn, I’d be like, “I want to deep throat a cock like that. That’s what works? I’ll do that.”
BENNET: Do I have to live up to it, or will I rebel against it?
DEL GAIZO: I feel like most people will try to live up to it rather than rebel.
LEHRER: Did you feel empowered at all doing the webcam stuff?
DEL GAIZO: Totally. You get a lot of compliments. [Laughs.] It’s a dichotomy. Even though no one had physically touched me, I would need to take a shower afterwards.
BENNETT: You’re technically in control, but you still have to navigate the levels of their control over you.
DEL GAIZO: It’s such a trick. I’ve always felt that you could use being objectified into something empowering. That’s always interested me as a concept.
BENNETT: We got so many unsolicited dick pics sent to us. Dudes, what are you thinking?
LEHRER: If you do that, you might end up in an art installation (laughs).
DEL GAIZO: It’s alarming how desensitized I became to seeing them.
BENNETT: Anna is a highly intelligent human being, a writer, a fully formed member of society. The minute this girl is on the webcam, the way that they communicate is so infantilizing.
DEL GAIZO: A lot of the guys would be like, “You’re actually really smart. Why are you doing this?”
LEHRER: Misogyny, much?
DEL GAIZO: People think that someone who willingly objectifies herself doesn’t deserve to get treated with respect. I understand the psychology.
BENNETT: Cops don’t investigate the murders of prostitutes the same way. They’re dehumanized. The character does the opposite. She is in control.
LEHRER: Is murder, in the metaphorical sense, empowering?
BENNETT: Totally.
DEL GAIZO: Do you know how many times I’ve fantasized about murdering guys?
BENNETT: The amount of times you’ve been disrespected, condescended to, dehumanized – you just want to flip out. Making this movie was therapeutic.
Click here to watch Remy Bennett and Anna del Gaizo's EAT ME. Text, interview and photographs by Adam Lehrer. Follow Autre on INSTAGRAM: @AUTREMAGAZINE